Portal:Phoenicia/Sandbox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Phoenicia/Sandbox
THE PHOENICIA PORTAL
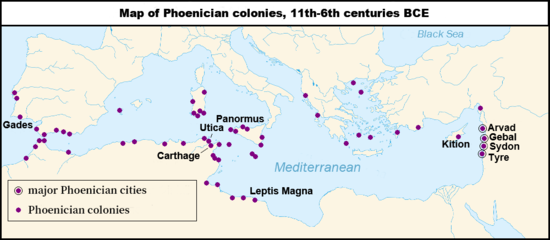
Phoenicia (/fəˈnɪʃə, fəˈniːʃə/), or Phœnicia, was an ancient Semitic thalassocratic civilization originating in the coastal strip of the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenicians expanded and contracted throughout history, with the core of their culture stretching from Arwad in modern Syria to Mount Carmel in modern Israel covering the entire coast of modern Lebanon. Beyond their homeland, the Phoenicians extended through trade and colonization throughout the Mediterranean, from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula.
The Phoenicians directly succeeded the Bronze Age Canaanites, continuing their cultural traditions following the decline of most major cultures in the Late Bronze Age collapse and into the Iron Age without interruption. It is believed that they self-identified as Canaanites and referred to their land as Canaan, indicating a continuous cultural and geographical association. The name Phoenicia is an ancient Greek exonym that did not correspond precisely to a cohesive culture or society as it would have been understood natively. Therefore, the division between Canaanites and Phoenicians around 1200 BC is regarded as a modern and artificial division.
The Phoenicians, known for their prowess in trade, seafaring and navigation, dominated commerce across classical antiquity and developed an expansive maritime trade network lasting over a millennium. This network facilitated cultural exchanges among major cradles of civilization like Greece, Egypt, and Mesopotamia. The Phoenicians established colonies and trading posts across the Mediterranean; Carthage, a settlement in northwest Africa, became a major civilization in its own right in the seventh century BC.
The Phoenicians were organized in city-states, similar to those of ancient Greece, of which the most notable were Tyre, Sidon, and Byblos. Each city-state was politically independent, and there is no evidence the Phoenicians viewed themselves as a single nationality. While most city-states were governed by some form of kingship, merchant families likely exercised influence through oligarchies. After reaching its zenith in the ninth century BC, the Phoenician civilization in the eastern Mediterranean gradually declined due to external influences and conquests. Yet, their presence persisted in the central and western Mediterranean until the destruction of Carthage in the mid-second century BC. — Read more about Phoenicia, its mythology and languagehttps://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Portal:Phoenicia/Sandbox&action=edit
Read or find an article
The Readers' FAQ and our about page contain the most commonly sought information about Wikipedia.
For simple searches, there is a search box at the top of every page. Type what you are looking for in the box. Partial matches will appear in a dropdown list. Select any page in the list to go to that page. Or, select the magnifying glass "Go" button, or press ↵ Enter, to go to a full search result. For advanced searches, see Help:Searching.
There are other ways to browse and explore Wikipedia articles; many can be found at Wikipedia:Contents. Also see our disclaimer for cautions about Wikipedia's limitations.
Edit an article
Contributing is easy: see how to edit a page. For a quick summary on participating, see contributing to Wikipedia, and for a friendly tutorial, see our introduction. For a listing of introductions and tutorials by topic, see getting started. The Simplified Manual of Style and Cheatsheet can remind you of basic wiki markup.
Be bold in improving articles! When adding facts, please provide references so others may verify them. If you are affiliated with the article subject, please see our conflict of interest guideline.
The simple guide to vandalism cleanup can help you undo malicious edits.
If you're looking for places you can help out, the Task Center is the place to go, or check out what else is happening at the community portal. You can practice editing and experiment in a sandboxyour sandbox.
,
 Featured article
-
Featured article
-
This is a Featured article, which represents some of the best content on English Wikipedia..
The law school of Berytus (also known as the law school of Beirut) was a center for the study of Roman law in classical antiquity located in Berytus (modern-day Beirut, Lebanon). It flourished under the patronage of the Roman emperors and functioned as the Roman Empire's preeminent center of jurisprudence until its destruction in AD 551.
The law schools of the Roman Empire established organized repositories of imperial constitutions and institutionalized the study and practice of jurisprudence to relieve the busy imperial courts. The archiving of imperial constitutions facilitated the task of jurists in referring to legal precedents. The origins of the law school of Beirut are obscure, but probably it was under Augustus in the first century. The earliest written mention of the school dates to 238–239 AD, when its reputation had already been established. The school attracted young, affluent Roman citizens, and its professors made major contributions to the Codex of Justinian. The school achieved such wide recognition throughout the Empire that Beirut was known as the "Mother of Laws". Beirut was one of the few schools allowed to continue teaching jurisprudence when Byzantine emperor Justinian I shut down other provincial law schools. (Full article...) Good article
-
Good article
-
This is a Good article, an article that meets a core set of high editorial standards.
The Battle of Ticinus was fought between the Carthaginian forces of Hannibal and a Roman army under Publius Cornelius Scipio in late November 218 BC as part of the Second Punic War. It took place in the flat country on the right bank of the river Ticinus, to the west of modern Pavia in northern Italy. Hannibal led 6,000 Libyan and Iberian cavalry, while Scipio led 3,600 Roman, Italian and Gallic cavalry and a large but unknown number of light infantry javelinmen.
War had been declared early in 218 BC over perceived infringements of Roman prerogatives in Iberia (modern Spain and Portugal) by Hannibal. Hannibal had gathered a large army, marched out of Iberia, through Gaul (modern France) and over the Alps into Cisalpine Gaul (northern Italy), where many of the local tribes were opposed to Rome. The Romans were taken by surprise, but one of the consuls for the year, Scipio, led an army along the north bank of the Po with the intention of giving battle to Hannibal. The two commanding generals each led out strong forces to reconnoitre their opponents. Scipio mixed many javelinmen with his main cavalry force, anticipating a large-scale skirmish. Hannibal put his close-order cavalry in the centre of his line, with his light Numidian cavalry on the wings. (Full article...)Selected Phoenician inscriptions and language articles -
The Corpus Inscriptionum Semiticarum ("Corpus of Semitic Inscriptions", abbreviated CIS) is a collection of ancient inscriptions in Semitic languages produced since the end of 2nd millennium BC until the rise of Islam. It was published in Latin. In a note recovered after his death, Ernest Renan stated that: "Of all I have done, it is the Corpus I like the most."
The first part was published in 1881, fourteen years after the beginning of the project. Renan justified the fourteen year delay in the preface to the volume, pointing to the calamity of the Franco-Prussian war and the difficulties that arose in the printing the Phoenician characters, whose first engraving was proven incorrect in light of the inscriptions discovered subsequently. A smaller collection – Répertoire d'Épigraphie Sémitique ("Repertory of Semitic Epigraphy", abbreviated RES) – was subsequently created to present the Semitic inscriptions without delay and in a deliberately concise way as they became known, and was published in French rather than Latin. The Répertoire was for the Corpus Inscriptionum Semiticarum what the Ephemeris epigraphica latina was for the Corpus Inscriptionum Latinarum.
The publication of the series continued until 1962. (Full article...)Selected Phoenician mythology articles -
Qetesh (also Qodesh, Qadesh, Qedesh, Qetesh, Kadesh, Kedesh, Kadeš or Qades /ˈkɑːdɛʃ/) was a goddess who was incorporated into the ancient Egyptian religion in the late Bronze Age. Her name was likely developed by the Egyptians based on the Semitic root Q-D-Š meaning 'holy' or 'blessed,' attested as a title of El and possibly Athirat and a further independent deity in texts from Ugarit.
Due to lack of clear references to Qetesh as a distinct deity in Ugaritic and other Syro-Palestinian sources, she is considered an Egyptian deity influenced by religion and iconography of Canaan by many modern researchers, rather than merely a Canaanite deity adopted by the Egyptians (examples of which include Reshef and Anat) (Full article...)General images
Categories
Related portals
Wikiproject
Other Wikimedia and Wikiportals
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Parent portal: Lebanon