User:Abyssal/Portal:Quaternary
IntroductionThe Quaternary (/kwəˈtɜːrnəri, ˈkwɒtərnɛri/ kwə-TUR-nə-ree, KWOT-ər-nerr-ee) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ago to the present. As of 2023, the Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene (2.58 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to today); a third epoch, the Anthropocene, has recently been proposed, but it is not officially recognised by the ICS. The Quaternary Period is typically defined by the cyclic growth and decay of continental ice sheets related to the Milankovitch cycles and the associated climate and environmental changes that they caused. (Full article...) Selected article on the Quaternary prehistory world and its legacies
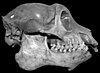
Mesopropithecus is an extinct genus of small to medium-sized lemur, or strepsirrhine primate, from Madagascar that includes three species, M. dolichobrachion, M. globiceps, and M. pithecoides. Together with Palaeopropithecus, Archaeoindris, and Babakotia, it is part of the sloth lemur family (Palaeopropithecidae). Once thought to be an indriid because its skull is similar to that of living sifakas, a recently discovered postcranial skeleton shows Mesopropithecus had longer forelimbs than hindlimbs—a distinctive trait shared by sloth lemurs but not by indriids. However, as it had the shortest forelimbs of all sloth lemurs, it is thought that Mesopropithecus was more quadrupedal and did not use suspension as much as the other sloth lemurs.
All three species ate leaves, fruits, and seeds, but the proportions were different. M. pithecoides was primarily a leaf-eater (folivores), but also ate fruit and occasionally seeds. M. globiceps ate a mix of fruits and leaves, as well as a larger quantity of seeds than M. pithecoides. M. dolichobrachion also consumed a mixed diet of fruits and leaves, but analysis of its teeth suggests that it was more of a seed predator than the other two species. (see more...) Selected article on the Quaternary prehistory in human science, culture and economics In 1858, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace published a new evolutionary theory that was explained in detail in Darwin's On the Origin of Species (1859). Unlike Lamarck, Darwin proposedcommon descent and a branching tree of life. The theory was based on the idea of natural selection, and it synthesized a broad range of evidence from animal husbandry, biogeography, geology, morphology, and embryology. The debate over Darwin's work led to the rapid acceptance of the general concept of evolution, but the specific mechanism he proposed, natural selection, was not widely accepted until it was revived by developments in biology that occurred during the 1920s through the 1940s. Before that time most biologists argued that other factors were responsible for evolution. The synthesis of natural selection with Mendelian genetics during the 1920s and 1930s founded the new discipline of population genetics. Throughout the 1930s and 1940s, population genetics became integrated with other biological fields, resulting in a widely applicable theory of evolution that encompassed much of biology—the modern evolutionary synthesis. (see more...) Selected image
Did you know?
Need help?Do you have a question about Abyssal/Portal:Quaternary that you can't find the answer to? Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk. TopicsGeochronology - Quaternary (Pleistocene - Holocene) Quaternary landmasses - Major Quaternary events - Quaternary biota appearances - Fossil sites - Stratigraphic units - History - History of paleontology - Timeline of paleontology Researchers - Culture - Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology - Vertebrate Paleontology Quality ContentFeatured Quaternary prehistory articles - Good Quaternary prehistory articles - SubcategoriesThings you can doRelated contentAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
|