Portal:History of science
The History of Science Portal
The history of science covers the development of science from ancient times to the present. It encompasses all three major branches of science: natural, social, and formal. Protoscience, early sciences, and natural philosophies such as alchemy and astrology during the Bronze Age, Iron Age, classical antiquity, and the Middle Ages declined during the early modern period after the establishment of formal disciplines of science in the Age of Enlightenment.
Science's earliest roots can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia around 3000 to 1200 BCE. These civilizations' contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine influenced later Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, wherein formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Latin-speaking Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but continued to thrive in the Greek-speaking Byzantine Empire. Aided by translations of Greek texts, the Hellenistic worldview was preserved and absorbed into the Arabic-speaking Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age. The recovery and assimilation of Greek works and Islamic inquiries into Western Europe from the 10th to 13th century revived the learning of natural philosophy in the West. Traditions of early science were also developed in ancient India and separately in ancient China, the Chinese model having influenced Vietnam, Korea and Japan before Western exploration. Among the Pre-Columbian peoples of Mesoamerica, the Zapotec civilization established their first known traditions of astronomy and mathematics for producing calendars, followed by other civilizations such as the Maya.
Natural philosophy was transformed during the Scientific Revolution in 16th- to 17th-century Europe, as new ideas and discoveries departed from previous Greek conceptions and traditions. The New Science that emerged was more mechanistic in its worldview, more integrated with mathematics, and more reliable and open as its knowledge was based on a newly defined scientific method. More "revolutions" in subsequent centuries soon followed. The chemical revolution of the 18th century, for instance, introduced new quantitative methods and measurements for chemistry. In the 19th century, new perspectives regarding the conservation of energy, age of Earth, and evolution came into focus. And in the 20th century, new discoveries in genetics and physics laid the foundations for new sub disciplines such as molecular biology and particle physics. Moreover, industrial and military concerns as well as the increasing complexity of new research endeavors ushered in the era of "big science," particularly after World War II. (Full article...)
Selected article -

The Discovery Expedition of 1901–1904, known officially as the British National Antarctic Expedition, was the first official British exploration of the Antarctic regions since the voyage of James Clark Ross sixty years earlier (1839–1843). Organized on a large scale under a joint committee of the Royal Society and the Royal Geographical Society (RGS), the new expedition carried out scientific research and geographical exploration in what was then largely an untouched continent. It launched the Antarctic careers of many who would become leading figures in the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, including Robert Falcon Scott who led the expedition, Ernest Shackleton, Edward Wilson, Frank Wild, Tom Crean and William Lashly.
Its scientific results covered extensive ground in biology, zoology, geology, meteorology and magnetism. The expedition discovered the existence of the only snow-free Antarctic valleys, which contains the longest river of Antarctica. Further achievements included the discoveries of the Cape Crozier emperor penguin colony, King Edward VII Land, and the Polar Plateau (via the western mountains route) on which the South Pole is located. The expedition tried to reach the South Pole travelling as far as the Farthest South mark at a reported 82°17′S. (Full article...)Selected image

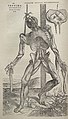
An allegorical anatomy engraving from Andreas Vesalius's De humani corporis fabrica (1543), imparting a moral lesson on the consequences of evil and a physical lesson on the internal structure of the body.
Did you know
...that the travel narrative The Malay Archipelago, by biologist Alfred Russel Wallace, was used by the novelist Joseph Conrad as a source for his novel Lord Jim?
...that the seventeenth century philosophers René Descartes, Baruch Spinoza, and Gottfried Leibniz, along with their Empiricist contemporary Thomas Hobbes all formulated definitions of conatus, an innate inclination of a thing to continue to exist and enhance itself?
...that according to the controversial Hockney-Falco thesis, the rise of realism in Renaissance art, such as Jan Van Eyck's Arnolfini Portrait (pictured), was largely due to the use of curved mirrors and other optical aids?
Selected Biography -

Tycho Brahe (/ˈtaɪkoʊ ˈbrɑː(h)i, - ˈbrɑː(hə)/ TY-koh BRAH-(h)ee, - BRAH(-hə), Danish: [ˈtsʰykʰo ˈpʁɑːə] ⓘ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe, Danish: [ˈtsʰyːjə ˈʌtəsn̩ ˈpʁɑːə]; 14 December 1546 – 24 October 1601), generally called Tycho for short, was a Dutch astronomer of the Renaissance, known for his comprehensive and unprecedentedly accurate astronomical observations. He was known during his lifetime as an astronomer, astrologer, and alchemist. He was the last major astronomer before the invention of the telescope.
In 1572, Tycho noticed a completely new star that was brighter than any star or planet. Astonished by the existence of a star that ought not to have been there, he devoted himself to the creation of ever more accurate instruments of measurement over the next fifteen years (1576–1591). King Frederick II granted Tycho an estate on the island of Hven and the money to build Uraniborg, the first large observatory in Christian Europe. He later worked underground at Stjerneborg, where he realised that his instruments in Uraniborg were not sufficiently steady. His unprecedented research program both turned astronomy into the first modern science and also helped launch the Scientific Revolution. (Full article...)Selected anniversaries
9 May
- 1931 - Death of Albert Abraham Michelson, Prussian-born American physicist and Nobel Prize laureate (b. 1852)
- 1950 - Death of Esteban Terradas i Illa, Catalan mathematician, scientist, and engineer (b. 1883
Related portals
Topics
General images
Subcategories
Things you can do
Help out by participating in the History of Science Wikiproject (which also coordinates the histories of medicine, technology and philosophy of science) or join the discussion.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus