User:Mr. Ibrahem/Meloxicam
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Mobic, Metacam, Anjeso, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601242 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, IV |
| Drug class | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 89%[2] |
| Protein binding | 99.4%[2] |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2C9 and 3A4-mediated)[2] |
| Elimination half-life | 20 hours[2] |
| Excretion | Urine and faeces equally[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
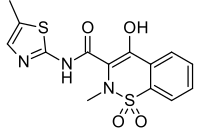
| Formula | C14H13N3O4S2 |
| Molar mass | 351.40 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Meloxicam, sold under the brand name Mobic among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammation in rheumatic diseases and osteoarthritis.[3][4] It is used by mouth or by injection into a vein.[4][6] It is recommended that it be used for as short a period as possible and at a low dose.[4]
Common side effects include abdominal pain, dizziness, swelling, headache, and a rash.[4] Serious side effects may include heart disease, stroke, kidney problems, and stomach ulcers.[4] Use is not recommended in the third trimester of pregnancy.[4] It blocks cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) more than it blocks cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1).[4] It is in the oxicam family of chemicals and is closely related to piroxicam.[4]
Meloxicam was patented in 1977 and approved for medical use in the United States in 2000.[4][7] It was developed by Boehringer Ingelheim, however it is also available as a generic medication.[4] In the United States the wholesale cost per dose is less than US$0.02 as of 2018[update].[8] In the United Kingdom it costs about 0.13 pounds as of 2018[update].[3] In 2017, it was the 38th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 19 million prescriptions.[9][10]
References[edit]
- ^ a b Use During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- ^ a b c d e Noble S, Balfour JA (March 1996). "Meloxicam". Drugs. 51 (3): 424–30, discussion 431–32. doi:10.2165/00003495-199651030-00007. PMID 8882380.
- ^ a b c British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 1112–1113. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Meloxicam Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. AHFS. Archived from the original on 23 December 2018. Retrieved 23 December 2018.
- ^ "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 27 November 2020. Retrieved 9 September 2020.
- ^ "Baudax Bio Announces FDA Approval of Anjeso for the Management of Moderate to Severe Pain". Baudax Bio, Inc. (Press release). 20 February 2020. Archived from the original on 21 February 2020. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
- ^ Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 519. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 10 July 2020. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- ^ "NADAC as of 2018-12-19". Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). Archived from the original on 19 December 2018. Retrieved 22 December 2018.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 12 February 2021. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ^ "Meloxicam Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. 23 December 2019. Archived from the original on 12 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
