User:SeemaaSaleh/sandbox
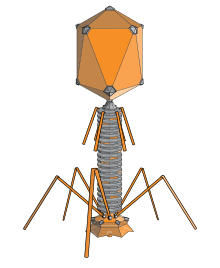
T-even phages, also known as the E. coli phages, are a group of double-stranded bacteriophages from the family Myoviridae. Bacteriophage means to "eat bacteria", and phages are well known for being obligate intracellular parasites that reproduce within the host cell and are released when the host is destroyed by lysis. Containing about 160 genes, these virulent viruses are among the largest, most complex viruses that are known and one of the best studied model organisms. Until today they have played a key role in the development of virology and molecular biology.
