User:PresN/mammals
Mammals are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (/məˈmeɪli.ə/), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla (cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others).
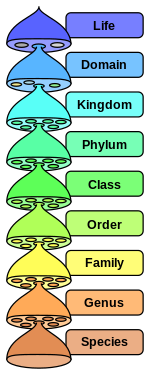
Mammals are divided into three main groupings: the order Monotremata, containing egg-laying species; the infraclass Placentalia, containing the vast majority of extant mammals, for which the fetus is carried in the uterus; and the infraclass Marsupialia, containing the marsupial animals wherein the young are carried in a pouch. Placentalia and Marsupialia are subdivided into superorders, which then contain multiple orders of animals. These orders can contain between one and hundreds of species, grouped into genera and then into families. Orders and superorders are also sometimes grouped into named clades.
Monotremata[edit]
Monotremata is the smallest of the three main divisions of mammals, containing only five extant species. It is distinguished from the other two groups in that the monotremes are egg-laying rather than bearing live young, but, like all mammals, the female monotremes nurse their young with milk.
Infraclass Placentalia[edit]
| Placentalia | |
Placentalia is one of the three main divisions of mammals, and contains the vast majority of extant species with around 5,500 species. It is distinguished from the other two groups in that the placental animals have fetuses that are carried in the uterus. It contains four superorders: Afrotheria, Euarchontoglires, Laurasiatheria, and Xenarthra; Afrotheria and Xenarthra make up the magnorder Atlantogenata, and the other two the magnorder Boreoeutheria.
Superorder Afrotheria[edit]
Afrosoricida[edit]
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chrysochloridae (Golden moles) |
Gray, 1825
21 species in 10 genera
|
Sub-Saharan Africa | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potamogalidae (Otter shrews) |
Allmann, 1865
Three species in two genera
|
Sub-Saharan Africa | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Tenrecidae (Tenrecs) |
Gray, 1821
31 species in 8 genera
|
Madagascar
|
Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
Hyracoidea[edit]
Macroscelidea[edit]
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Macroscelididae (Elephant shrews) |
Bonaparte, 1838
Nineteen species in six genera
|
Africa | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
Proboscidea[edit]
Sirenia[edit]
Tubulidentata[edit]
Superorder Euarchontoglires[edit]
Scandentia[edit]
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ptilocercidae (Pen-tailed treeshrews) |
Lyon, 1913
One species in one genera
|
Southeast Asia
|
Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Tupaiidae (Treeshrews) |
Gray, 1825
22 species in 3 genera
|
India and Southeast Asia | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
Dermoptera[edit]
Lagomorpha[edit]
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leporidae (Hares and rabbits) |
G. Fischer von Waldheim, 1817
64 species in 11 genera (full list)
|
Worldwide | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Ochotonidae (Pikas) |
Thomas, 1897
29 species in 1 genera (full list)
|
Asia and western North America | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
Primates[edit]
Rodentia[edit]
Superorder Laurasiatheria[edit]
Artiodactyla[edit]
Carnivora[edit]
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ailuridae (Red panda) |
Gray, 1843
Two species in one genus
|
Eastern Himalayas and southwestern China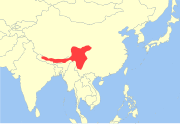
|
Size range: 50–64 cm (20–25 in) long, plus 28–59 cm (11–23 in) tail[1] Habitats: Forest and shrubland[2] Diets: Bamboo, as well as fruit, vegetation, lichen, bird eggs, and insects[2] |
| Canidae (Wolves and foxes) |
Waldheim, 1817
37 species in 14 genera (full list)
|
Worldwide | Size range: 33 cm (13 in) long, plus 13 cm (5 in) tail (fennec fox) to 160 cm (63 in) long, plus 50 cm (20 in) tail (wolf) Habitats: Shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, forest, desert, rocky areas, savanna, desert, and coastal marine Diets: Omnivorous |
| Mephitidae (Skunks and stink badgers) |
Geoffroy and Cuvier, 1795
|
North America, South America, Southeast Asia
|
Size range: Habitats: Diets: Omnivorous; primarily eats invertebrates, rodents, small reptiles, and eggs |
| Mustelidae (Martens, polecats, otters, and badgers) |
Geoffroy and Cuvier, 1795
63 species in 23 genera (full list)
|
All continents except Antarctica and Australia | Size range: Habitats: Diets: Omnivorous |
| Odobenidae (Walrus) |
Allen, 1880
|
Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas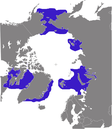
|
Size range: Male: 270–356 cm (106–140 in) long; 800–1,700 kg (1,764–3,748 lb) Female: 225–312 cm (89–123 in) long; 400–1,250 kg (882–2,756 lb)[3] Habitats: Neritic marine, oceanic marine, intertidal marine, coastal marine, and other[4] Diets: Bivalve molluscs, as well as other invertebrates, slow-moving fish, and occasionally birds, seals, and other marine mammals[4] |
| Otariidae (Eared seals) |
Gray, 1825
Sixteen species in seven genera (full list)
|
Antarctic Ocean, southern seas, and coasts of South America, Australia, Pacific Asia and Pacific North America | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Phocidae (Earless seals) |
Gray, 1821
Nineteen species in fourteen genera (full list)
|
Antarctic Ocean, Arctic Ocean, Northern Hemisphere coastlines, Caspian Sea, and Lake Baikal | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Procyonidae (Raccoons, coatis, olingos, kinkajous, ring-tailed cats, and cacomistles) |
Gray, 1825
Fourteen species in six genera (full list)
|
North and South America (common raccoon introduced to Europe, western Asia, and Japan) | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Ursidae (Bears) |
G. Fischer von Waldheim, 1817
Eight species in five genera (full list)
|
North and South America and Eurasia | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eupleridae (Malagasy carnivorans) |
Chenu, 1850
Ten species in seven genera
|
Madagascar
|
Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Felidae (Cats) |
G. Fischer von Waldheim, 1817
41 species in 14 genera (full list)
|
Worldwide (Felinae (excluding the domestic cat) in blue, Pantherinae in green
|
Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Herpestidae (Mongooses) |
Bonaparte, 1845
34 species in 14 genera (full list)
|
Southern Europe, Africa, and Asia
|
Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Hyaenidae (Hyenas) |
Gray, 1821
Four species in four genera
|
Africa and southern Asia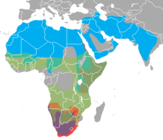
|
Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Nandiniidae (African palm civet) |
Pocock, 1929
One species in one genus
|
Sub-Saharan Africa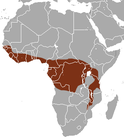
|
Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Prionodontidae (Asiatic linsangs) |
Gray, 1864
Two species in one genus
|
Southeast Asia | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Viverridae (Civets and genets) |
Gray, 1821
33 species in 14 genera (full list)
|
Southeast Asia | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
Chiroptera[edit]
Eulipotyphla[edit]
Perissodactyla[edit]
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rhinocerotidae (Rhinoceroses) |
Owen, 1845
Five species in four genera
|
Sub-Saharan Africa, northern India, Southeast Asia | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Tapiridae (Tapirs) |
Brünnich, 1772
Four species in one genus
|
South America, Central America, scattered southeastern Asia | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equidae (Horses, donkeys, zebras) |
Brünnich, 1772
|
Worldwide | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
Pholidota[edit]
Superorder Xenarthra[edit]
Cingulata[edit]
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dasypodidae (Armadillos) |
Gray, 1821
Nine species in one genus
|
South America, and central, southern, and eastern North America | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Chlamyphoridae (Armadillos) |
Bonaparte, 1850
Thirteen species in eight genera
|
South America and Central America | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
Pilosa[edit]
Infraclass Marsupialia[edit]

Marsupialia is one of the three main divisions of mammals, and contains around 300 extant species. It is distinguished from the other two groups in that marsupials give birth to relatively undeveloped young that often reside in a pouch located on their mothers' abdomen for a certain amount of time. It contains two superorders, Ameridelphia and Australidelphia.
Superorder Australidelphia[edit]
Dasyuromorphia[edit]
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dasyuridae (Marsupial shrews) |
Goldfuss, 1820
71 species in 13 genera
|
Australia and New Guinea | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Myrmecobiidae (Numbat) |
Waterhouse, 1841
One species in one genus
|
Scattered Australia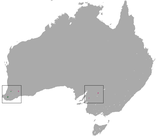
|
Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Thylacinidae† (Thylacine) |
C. L. Bonaparte, 1838
One species in one genus
|
Tasmania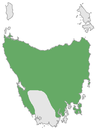
|
Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
Diprotodontia[edit]
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypsiprymnodontidae (musky rat-kangaroo) |
Collett, 1877
1 species in 1 genera
|
Northeastern Australia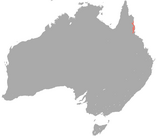
|
Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Macropodidae | Gray, 1821
64 species in 13 genera
|
Australia and New Guinea | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Potoroidae | Gray, 1821
Eight species in three genera
|
Australia | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acrobatidae | Aplin, 1987
Two species in two genera
|
Eastern Australia and New Guinea | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Burramyidae | Broom, 1989
Two species in two genera
|
New Guinea and southern and northeastern Australia | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Petauridae | C. L. Bonaparte, 1838
Eleven species in three genera
|
New Guinea and northern, eastern, and southern Australia | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Phalangeridae | Thomas, 1888
27 species in 6 genera
|
New Guinea, Sulawesi island and nearby islands in Indonesia, and scattered Australia | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Pseudocheiridae (ringtail possum) |
Winge, 1893
Eleven species in three genera
|
New Guinea and northern, eastern, and southern Australia | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Tarsipedidae (ringtail possum) |
Gervais, Verreaux, 1842
One species in one genus
|
Southwestern Australia
|
Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phascolarctidae (koala) |
Owen, 1839
One species in one genus
|
Southern and eastern Australia | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
| Vombatidae (wombat) |
Burnett, 1830
Three species in two genera
|
Eastern Australia
|
Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
Microbiotheria[edit]
Notoryctemorphia[edit]
Paucituberculata[edit]
Peramelemorphia[edit]
Other[edit]
Didelphimorphia[edit]
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Didelphidae (Opossums) |
Gray, 1821
93 species in 18 genera
|
North America and South America | Size range: Habitats: Diets: |
Paucituberculata[edit]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Redpandasizewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
IUCNRedpandawas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Walkerswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
IUCNWalruswas invoked but never defined (see the help page).












































