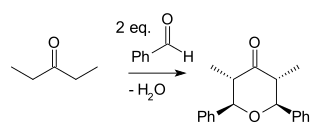
Japp–Maitland condensation
The Japp–Maitland condensation is an organic reaction and a type of Aldol reaction and a tandem reaction. In a reaction between the ketone 2-pentanone and the aldehyde benzaldehyde catalyzed by base the bis Aldol adduct is formed first. The second step is a ring-closing reaction when one hydroxyl group displaces the other in a nucleophilic substitution forming an oxo-tetrahydropyran.
The reaction was first described by Francis Robert Japp and William Maitland in 1904.[1]
The Japp–Maitland reaction is of some importance to synthetic organic chemistry for example as part of the synthesis of biomolecule centrolobine:[2][3]
References[edit]
- ^ CXLVIII.—Reduction products of -dimethylanhydracetonebenzil, and condensation products of benzaldehyde with ketones Francis Robert Japp F.R.S. and William Maitland BSc J. Chem. Soc. , Trans., 1904, 85, 1473–89, doi:10.1039/CT9048501473
- ^ Exploiting the Maitland–Japp reaction: a synthesis of (G)-centrolobine Paul A. Clarke and William H. C. Martin Tetrahedron 61 (2005) 5433–38 doi:10.1016/j.tet.2005.04.011
- ^ 2-step procedure, step one is a Mukaiyama aldol reaction. The catalyst in step two is boron trifluoride TMS = trimethylsilyl TBS = tert-butyldimethylsilyl