Portal:Phoenicia
THE PHOENICIA PORTAL
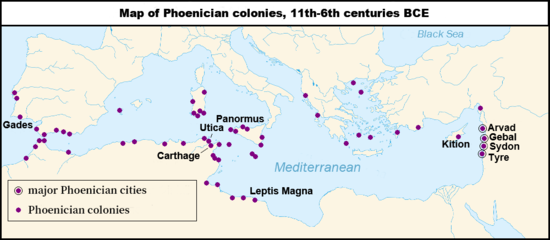
Phoenicia (/fəˈnɪʃə, fəˈniːʃə/), or Phœnicia, was an ancient Semitic thalassocratic civilization originating in the coastal strip of the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenicians expanded and contracted throughout history, with the core of their culture stretching from Arwad in modern Syria to Mount Carmel in modern Israel covering the entire coast of modern Lebanon. Beyond their homeland, the Phoenicians extended through trade and colonization throughout the Mediterranean, from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula.
The Phoenicians directly succeeded the Bronze Age Canaanites, continuing their cultural traditions following the decline of most major cultures in the Late Bronze Age collapse and into the Iron Age without interruption. It is believed that they self-identified as Canaanites and referred to their land as Canaan, indicating a continuous cultural and geographical association. The name Phoenicia is an ancient Greek exonym that did not correspond precisely to a cohesive culture or society as it would have been understood natively. Therefore, the division between Canaanites and Phoenicians around 1200 BC is regarded as a modern and artificial division.
The Phoenicians, known for their prowess in trade, seafaring and navigation, dominated commerce across classical antiquity and developed an expansive maritime trade network lasting over a millennium. This network facilitated cultural exchanges among major cradles of civilization like Greece, Egypt, and Mesopotamia. The Phoenicians established colonies and trading posts across the Mediterranean; Carthage, a settlement in northwest Africa, became a major civilization in its own right in the seventh century BC.
The Phoenicians were organized in city-states, similar to those of ancient Greece, of which the most notable were Tyre, Sidon, and Byblos. Each city-state was politically independent, and there is no evidence the Phoenicians viewed themselves as a single nationality. While most city-states were governed by some form of kingship, merchant families likely exercised influence through oligarchies. After reaching its zenith in the ninth century BC, the Phoenician civilization in the eastern Mediterranean gradually declined due to external influences and conquests. Yet, their presence persisted in the central and western Mediterranean until the destruction of Carthage in the mid-second century BC. — Read more about Phoenicia, its mythology and language
 Featured article
•
Featured article
•
A Featured article represents some of the best content on Wikipedia
The Battle of Panormus was fought in Sicily in 250 BC during the First Punic War between a Roman army led by Lucius Caecilius Metellus and a Carthaginian force led by Hasdrubal, son of Hanno. The Roman force of two Roman and two allied legions defending the city of Panormus defeated the much larger Carthaginian army of 30,000 men and between 60 and 142 war elephants.
The war had commenced in 264 BC with Carthage in control of much of Sicily, where most of the fighting took place. In 256–255 BC the Romans attempted to strike at the city of Carthage in North Africa, but suffered a heavy defeat by a Carthaginian army strong in cavalry and elephants. When the focus of the war returned to Sicily, the Romans captured the large and important city of Panormus in 254 BC. Thereafter they avoided battle for fear of the war elephants which the Carthaginians had shipped to Sicily. In late summer 250 BC Hasdrubal led out his army to devastate the crops of the cities of Rome's allies. The Romans withdrew to Panormus and Hasdrubal pressed on to the city walls. (Full article...)Phoenician mythology •
Astarte (/əˈstɑːrtiː/; Ἀστάρτη, Astartē) is the Hellenized form of the Ancient Near Eastern goddess ʿAṯtart. ʿAṯtart was the Northwest Semitic equivalent of the East Semitic goddess Ishtar.
Astarte was worshipped from the Bronze Age through classical antiquity, and her name is particularly associated with her worship in the ancient Levant among the Canaanites and Phoenicians, though she was originally associated with Amorite cities like Ugarit and Emar, as well as Mari and Ebla. She was also celebrated in Egypt, especially during the reign of the Ramessides, following the importation of foreign cults there. Phoenicians introduced her cult in their colonies on the Iberian Peninsula. (Full article...)Images
 Good article
•
Good article
•
A Good article meets a core set of high editorial standards
Hasdrubal (fl. 255 – 250 BC) was a Carthaginian general who served during the middle years of the First Punic War, fought between Carthage and Rome, and took a leading part in three of the four major field battles of the war. He was a citizen of the city state of Carthage, which was in what is now Tunisia. His date of birth and age at death are both unknown, as are his activities prior to his coming to prominence in 255 BC. Modern historians distinguish him from other Carthaginians named Hasdrubal by the cognomen "son of Hanno".
Hasdrubal was one of three Carthaginian generals, possibly the senior, who took command of the army raised when the Romans invaded North Africa in 255 BC. He was responsible for the decision to march against the Romans late in the year and was present at the Battle of Adys where the Carthaginians were routed. Early in 254 BC the triumvirate of Carthaginian generals gave control of the army to the Spartan mercenary commander, Xanthippus, and accompanied him when the Romans were decisively beaten at the Battle of Tunis. (Full article...)Phoenician inscriptions & language •
The Cippi of Melqart are a pair of Phoenician marble cippi that were unearthed in Malta under undocumented circumstances and dated to the 2nd century BC. These are votive offerings to the god Melqart, and are inscribed in two languages, Ancient Greek and Phoenician, and in the two corresponding scripts, the Greek and the Phoenician alphabet. They were discovered in the late 17th century, and the identification of their inscription in a letter dated 1694 made them the first Phoenician writing to be identified and published in modern times. Because they present essentially the same text (with some minor differences), the cippi provided the key to the modern understanding of the Phoenician language. In 1758, the French scholar Jean-Jacques Barthélémy relied on their inscription, which used 17 of the 22 letters of the Phoenician alphabet, to decipher the unknown language.
The tradition that the cippi were found in Marsaxlokk was only inferred by their dedication to Heracles, whose temple in Malta had long been identified with the remains at Tas-Silġ. The Grand Master of the Order of the Knights Hospitaller, Fra Emmanuel de Rohan-Polduc, presented one of the cippi to the Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres in 1782. This cippus is currently in the Louvre Museum in Paris, while the other rests in the National Museum of Archaeology in Valletta, Malta. The inscription is known as KAI 47. (Full article...)Did you know (auto-generated) •

- ... that the earliest-known Phoenician inscriptions were found near Bethlehem?
- ... that the sarcophagus of Eshmunazar II, the Phoenician king of Sidon, is one of only three ancient Egyptian sarcophagi unearthed outside Egypt?
- ... that alongside a 7th-century BC Phoenician shipwreck, two additional wrecks from various historical periods were unearthed in Bajo de la Campana, situated off the coast of Cartagena, Spain?
- ... that the discovery of Phoenician metal bowls in 1849 created the entire concept of Phoenician art?
- ... that coins issued by Baalshillem II, the Phoenician king of Sidon, were the first Sidonian coins to bear minting dates corresponding to the king's year of reign?
- ... that Eshmunazar I, the Phoenician king of Sidon, participated in the Neo-Babylonian campaigns against Egypt, where he seized stone sarcophagi belonging to members of the Egyptian elite?
Related portals
Categories
Wikiproject
Other Wikimedia and Wikiportals
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Parent portal: Lebanon