Tracheotomy
| Tracheotomy | |
|---|---|
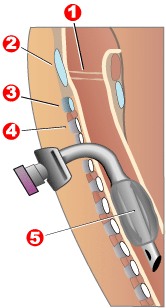 Completed tracheotomy: 1 – Vocal folds | |
| ICD-10-PCS | 0B110F4 |
| ICD-9-CM | 31.1 |
| MeSH | D014140 |
| MedlinePlus | 002955 |
Tracheotomy (/ˌtreɪkiˈɒtəmi/, UK also /ˌtræki-/), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The resulting stoma (hole) can serve independently as an airway or as a site for a tracheal tube or tracheostomy tube[1] to be inserted; this tube allows a person to breathe without the use of the nose or mouth.
Etymology and terminology[edit]

The etymology of the word tracheotomy comes from two Greek words: the root tom- (from Greek τομή tomḗ) meaning "to cut", and the word trachea (from Greek τραχεία tracheía).[2] The word tracheostomy, including the root stom- (from Greek στόμα stóma) meaning "mouth", refers to the making of a semi-permanent or permanent opening and to the opening itself. Some sources offer different definitions of the above terms. Part of the ambiguity is due to the uncertainty of the intended permanence of the stoma (hole) at the time it is created.[3]
Indications[edit]
There are four main reasons why someone would receive a tracheotomy:[3]
- Emergency airway access
- Airway access for prolonged mechanical ventilation
- Functional or mechanical upper airway obstruction
- Decreased/incompetent clearance of tracheobronchial secretions
In the acute (short term) setting, indications for tracheotomy include such conditions as severe facial trauma, tumors of the head and neck (e.g., cancers, branchial cleft cysts), and acute angioedema and inflammation of the head and neck. In the context of failed tracheal intubation, either tracheotomy or cricothyrotomy may be performed.[citation needed]

In the chronic (long-term) setting, indications for tracheotomy include the need for long-term mechanical ventilation and tracheal toilet (e.g., comatose patients, extensive surgery involving the head and neck). Tracheotomy may result in a significant reduction in the administration of sedatives and vasopressors, as well as the duration of stay in the intensive care unit (ICU).[4]
In extreme cases, the procedure may be indicated as a treatment for severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) seen in patients intolerant of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy. The reason tracheostomy works well for OSA is because it is the only surgical procedure that completely bypasses the upper airway. This procedure was commonly performed for obstructive sleep apnea until the 1980s, when other procedures such as the uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, genioglossus advancement, and maxillomandibular advancement surgeries were described as alternative surgical modalities for OSA.
If prolonged ventilation is required, tracheostomy is usually considered. The timing of this procedure is dependent on the clinical situation and an individual's preference. An international multicenter study in 2000 determined that the median time between starting mechanical ventilation and receiving a tracheostomy was 11 days.[5] Although the definition varies depending on hospital and provider, early tracheostomy can be considered to be less than 10 days (2 to 14 days) and late tracheostomy to be 10 days or more.
Alternatives[edit]
Biphasic cuirass ventilation is a form of non-invasive mechanical ventilation that can — in a small subset of cases — allow people to avoid a tracheostomy.[6]
Components[edit]

A tracheostomy tube may be single or dual lumen, and also cuffed or uncuffed. A dual lumen tracheostomy tube consists of an outer cannula or main shaft, an inner cannula, and an obturator. The obturator is used when inserting the tracheostomy tube to guide the placement of the outer cannula and is removed once the outer cannula is in place. The outer cannula remains in place but, because of the buildup of secretions, there is an inner cannula that may be removed for cleaning after use or it may be replaced. Single-lumen tracheostomy tubes do not have a removable inner cannula, suitable for narrower airways. Cuffed tracheostomy tubes have inflatable balloons at the end of the tube to secure them in place. A tracheostomy tube may be fenestrated with one or several holes to let air through the larynx, allowing speech.[7]
Special tracheostomy tube valves (such as the Passy-Muir valve[8]) have been created to assist people in their speech. The patient can inhale through the unidirectional tube. Upon expiration, pressure causes the valve to close, redirecting air around the tube, past the vocal folds, producing sound.[9]
Surgical procedure[edit]
Open surgical tracheotomy (OST)[edit]
The typical procedure done is the open surgical tracheotomy (OST) and is usually done in a sterile operating room. The optimal patient position involves a cushion under the shoulders to extend the neck. Commonly a transverse (horizontal) incision is made two fingerbreadths above the suprasternal notch. Alternatively, a vertical incision can be made in the midline of the neck from the thyroid cartilage to just above the suprasternal notch. Skin, subcutaneous tissue, and strap muscles (a specific group of neck muscles) are retracted aside to expose the thyroid isthmus, which can be cut or retracted upwards. After proper identification of the cricoid cartilage and placement of a tracheal hook to steady the trachea and pull it forward, the trachea is cut open, either through the space between cartilage rings or vertically across multiple rings (cruciate incision). Occasionally a section of a tracheal cartilage ring may be removed to make insertion of the tube easier. Once the incision is made, a properly sized tube is inserted. The tube is connected to a ventilator and adequate ventilation and oxygenation is confirmed. The tracheotomy apparatus is then attached to the neck with tracheotomy ties, skin sutures, or both.[10][11]
Percutaneous dilatational tracheotomy (PDT)[edit]
The first widely accepted percutaneous tracheotomy technique was described by Pat Ciaglia, a New York surgeon, in 1985.[12] The next widely used technique was developed in 1989 by Bill Griggs, an Australian intensive care specialist.[13] In 1995, Fantoni developed a translaryngeal approach of percutaneous tracheostomy.[14] The Griggs and Ciaglia Blue Rhino techniques are the two main techniques in current use. A number of comparison studies have been undertaken between these two techniques with no clear differences emerging[15] An advantage of PDT over OST is the ability to perform the procedure at the patient's bedside. This significantly decreases costs and time/people-power needed for an operating room (OR) procedure.[11] Contraindications for percutaneous tracheostomy include infection at the site of tracheostomy, uncontrolled bleeding disorder, unstable cardiopulmonary status, patient unable to stay still, abnormal anatomy of the tracheolaryngeal structures.[2]
Risks and complications[edit]
As with most other surgical procedures, some cases are more difficult than others. Surgery on children is more difficult because of their smaller size. Difficulties such as a short neck and bigger thyroid glands make the trachea hard to open.[16] There are other difficulties with patients with irregular necks, the obese, and those with a large goitre.
The many possible complications include hemorrhage, loss of airway, subcutaneous emphysema, wound infections, stomal cellulites, fracture of tracheal rings, poor placement of the tracheostomy tube, and bronchospasm.[17]
Early complications include infection, hemorrhage, pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax, tracheoesophageal fistula, recurrent laryngeal nerve injury, and tube displacement. Delayed complications include tracheal-innominate artery fistula, tracheal stenosis, delayed tracheoesophageal fistula, and tracheocutaneous fistula.[10]
A 2013 systematic review (published cases from 1985 to April 2013) studied the complications and risk factors of percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy (PDT), identifying major causes of fatality to be hemorrhage (38.0%), airway complications (29.6%), tracheal perforation (15.5%), and pneumothorax (5.6%)[18] A similar systematic review in 2017 (cases from 1990 to 2015) studying fatality in both open surgical tracheotomy (OST) and PDT identified similar rates of mortality and causes of death between the two techniques.[19]
Hemorrhage is rare, but the most likely cause of fatality after a tracheostomy. It usually occurs due to a tracheoarterial fistula, an abnormal connection between the trachea and nearby blood vessels, and most commonly manifests between 3 days to 6 weeks after the procedure is done. Fistulas can result from incorrectly positioned equipment, high cuff pressures causing pressure sores or mucosal damage, a low surgical trachea site, repetitive neck movement, radiotherapy, or prolonged intubation.[20]
A potential risk factor identified in a 2013 systematic review of the percutaneous technique was the lack of bronchoscopic guidance. Use of the bronchoscope, an instrument inserted through a patient's mouth for internal visualization of the airway, can help with proper placement of instruments and better visualization of anatomical structures. However, this can also be dependent on the skills and familiarity of the surgeon with both the procedure and the patient's anatomy.[18]
There are a multitude of potential complications related to the airway. The main causes of mortality during PDT include dislodgment of the tube, loss of airway during procedure and misplacement of the tube.[18] One of the more urgent complications include displacement or dislodgment of the tracheotomy tube, either spontaneously or during a tube change. Although uncommon (< 1/1000 tracheostomy tube days), the associated fatality is high due to the loss of airway.[21] Due to the seriousness of such a situation, individuals with a tracheotomy tube should consult with their healthcare providers to have a specific, written, emergency intubation and tracheostomy recannulation (reinsertion) plan prepared in advance.
Tracheal stenosis, otherwise known as an abnormal narrowing of the airway, is a possible long term complication. The most common symptom of stenosis is gradually-worsening difficulty with breathing (dyspnea). However incidence is low, ranging from 0.6 to 2.8% with increased rates if major bleeding or wound infections are present. A 2016 systematic review identified a higher rate of tracheal stenosis in individuals who underwent a surgical tracheostomy, as compared to PDT, however the difference was not statistically significant.[22]
A 2000 Spanish study of bedside percutaneous tracheostomy reported overall complication rates of 10–15% and a procedural mortality of 0%,[23] which is comparable to those of other series reported in the literature from the Netherlands[24][25] and the United States.[26][27] A 2013 systematic review calculated procedural mortality to be 0.17% or 1 in 600 cases.[18] Multiple systematic reviews identified no significant difference in rates of mortality, major bleeding, or wound infection between the percutaneous or open surgical methods.[22][19]
Specifically a 2017 systematic review calculated the most common causes of death and their frequencies, out of all tracheotomies, to be hemorrhage (OST: 0.26%, PDT: 0.19%), loss of airway (OST: 0.21%, PDT: 0.20%), and misplacement of tube (OST: 0.11%, PDT: 0.20%).[19]
A 2003 American cadaveric study identified multiple tracheal ring fractures with the Ciaglia Blue Rhino technique as a complication occurring in 100% of their small series of cases.[28] The comparative study above also identified ring fractures in 9 of 30 live patients[15] while another small series identified ring fractures in 5 of their 20 patients.[29] The long term significance of tracheal ring fractures is unknown.[citation needed]
History[edit]

Ancient history[edit]
Tracheotomy was first potentially depicted on Egyptian artifacts in 3600 BC.[30] Hippocrates condemned the practice of tracheotomy as incurring an unacceptable risk of damage to the carotid artery. Warning against the possibility of death from inadvertent laceration of the carotid artery during tracheotomy, he instead advocated the practice of tracheal intubation.[17]
Despite the concerns of Hippocrates, it is believed that an early tracheotomy was performed by Asclepiades of Bithynia, who lived in Rome around 100 BC.[31] Galen and Aretaeus, both of whom lived in Rome in the 2nd century AD, credit Asclepiades as being the first physician to perform a non-emergency tracheotomy. Antyllus, another Roman-era Greek physician of the 2nd century AD, supported tracheotomy when treating oral diseases. He refined the technique to be more similar to that used in modern times, recommending that a transverse incision be made between the third and fourth tracheal rings for the treatment of life-threatening airway obstruction.[17]
Medieval world[edit]
The 7th century Byzantine physician Paul of Aegina, an advocate of the procedure, acknowledged previous Greek authors' works on the subject of tracheotomies and provided descriptions of the procedure in his own works.[32] In 1000, Abu al-Qasim al-Zahrawi (936–1013), an Arab who lived in Arabic Spain, published the 30-volume Kitab al-Tasrif, the first illustrated work on surgery. He never performed a tracheotomy, but he did treat a slave girl who had cut her own throat in a suicide attempt. Al-Zahrawi (known to Europeans as Albucasis) sewed up the wound and the girl recovered, thereby proving that an incision in the larynx could heal. Circa AD 1020, Avicenna (980–1037) described tracheal intubation in The Canon of Medicine in order to facilitate breathing.[33] The first clear description of the tracheotomy operation for treating asphyxiation was given by Ibn Zuhr (1091–1161) in the 12th century. According to Mostafa Shehata, Ibn Zuhr (also known as Avenzoar) successfully practiced the tracheotomy procedure on a goat, justifying Galen's approval of the operation.[34]
16th–18th centuries[edit]

The European Renaissance brought with it significant advances in all scientific fields, particularly surgery. Increased knowledge of anatomy was a major factor in these developments. Surgeons became increasingly open to experimental surgery on the trachea. During this period, many surgeons attempted to perform tracheotomies, for various reasons and with various methods. Many suggestions were put forward, but little actual progress was made toward making the procedure more successful. The tracheotomy remained a dangerous operation with a very low success rate,[quantify] and many surgeons still considered the tracheotomy to be a useless and dangerous procedure. The high mortality rate[quantify] for this operation, which had not improved, supported their position. From the period 1500 to 1832 there are only 28 known reports of tracheotomy.[35]
In 1543, Andreas Vesalius (1514–1564) wrote that tracheal intubation and subsequent artificial respiration could be life-saving. Antonio Musa Brassavola (1490–1554) of Ferrara treated a patient with peritonsillar abscess by tracheotomy after the patient had been refused by barber surgeons. The patient apparently made a complete recovery, and Brassavola published his account in 1546. This operation has been identified as the first recorded successful tracheostomy, despite many ancient references to the trachea and possibly to its opening.[35] Ambroise Paré (1510–1590) described suture of tracheal lacerations in the mid-16th century. One patient survived despite a concomitant injury to the internal jugular vein. Another sustained wounds to the trachea and esophagus and died.
Towards the end of the 16th century, anatomist and surgeon Hieronymus Fabricius (1533–1619) described a useful technique for tracheotomy in his writings, although he had never actually performed the operation himself. He advised using a vertical incision and was the first to introduce the idea of a tracheostomy tube. This was a straight, short cannula that incorporated wings to prevent the tube from advancing too far into the trachea. He recommended the operation only as a last resort, to be used in cases of airway obstruction by foreign bodies or secretions. Fabricius' description of the tracheotomy procedure is similar to that used today. Giulio Cesare Casseri (1552–1616) succeeded Fabricius as professor of anatomy at the University of Padua and published his own writings regarding technique and equipment for tracheotomy. Casseri recommended using a curved silver tube with several holes in it. Marco Aurelio Severino (1580–1656), a skillful surgeon and anatomist, performed multiple successful tracheotomies during a diphtheria epidemic in Naples in 1610, using the vertical incision technique recommended by Fabricius. He also developed his own version of a trocar.[36]
In 1620 the French surgeon Nicholas Habicot (1550–1624), surgeon of the Duke of Nemours and anatomist, published a report of four successful "bronchotomies" which he had performed.[37] One of these is the first recorded case of a tracheotomy for the removal of a foreign body, in this instance a blood clot in the larynx of a stabbing victim. He also described the first tracheotomy to be performed on a pediatric patient. A 14-year-old boy swallowed a bag containing 9 gold coins in an attempt to prevent its theft by a highwayman. The object became lodged in his esophagus, obstructing his trachea. Habicot suggested that the operation might also be effective for patients with inflammation of the larynx. He developed equipment for this surgical procedure which displayed similarities to modern designs (except for his use of a single-tube cannula).[citation needed]
Sanctorius (1561–1636) is believed to be the first to use a trocar in the operation, and he recommended leaving the cannula in place for a few days following the operation.[38] Early tracheostomy devices are illustrated in Habicot's Question Chirurgicale[37] and Casseri's posthumous Tabulae anatomicae in 1627.[39] Thomas Fienus (1567–1631), Professor of Medicine at the University of Louvain, was the first to use the word "tracheotomy" in 1649, but this term was not commonly used until a century later.[40] Georg Detharding (1671–1747), professor of anatomy at the University of Rostock, treated a drowning victim with tracheostomy in 1714.[41][42][43]
19th century[edit]
In the 1820s, the tracheotomy began to be recognized as a legitimate means of treating severe airway obstruction. In 1832, French physician Pierre Bretonneau employed it as a last resort to treat a case of diphtheria.[44] In 1852, Bretonneau's student Armand Trousseau reported a series of 169 tracheotomies (158 of which were for croup, and 11 for "chronic maladies of the larynx")[45] In 1858, John Snow was the first to report tracheotomy and cannulation of the trachea for the administration of chloroform anesthesia in an animal model.[46] In 1871, the German surgeon Friedrich Trendelenburg (1844–1924) published a paper describing the first successful elective human tracheotomy to be performed for the purpose of administration of general anesthesia.[47] In 1880, the Scottish surgeon William Macewen (1848–1924) reported on his use of orotracheal intubation as an alternative to tracheotomy to allow a patient with glottic edema to breathe, as well as in the setting of general anesthesia with chloroform.[48][49] At last, in 1880 Morell Mackenzie's book discussed the symptoms indicating a tracheotomy and when the operation is absolutely necessary.[17]
20th century[edit]

In the early 20th century, physicians began to use the tracheotomy in the treatment of patients affected by paralytic poliomyelitis who required mechanical ventilation. However, surgeons continued to debate various aspects of the tracheotomy well into the 20th century. Many techniques were described and employed, along with many different surgical instruments and tracheal tubes. Surgeons could not seem to reach a consensus on where or how the tracheal incision should be made, arguing whether the "high tracheotomy" or the "low tracheotomy" was more beneficial. The currently used surgical tracheotomy technique was described in 1909 by Chevalier Jackson of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Jackson emphasised the importance of postoperative care, which dramatically reduced the death rate. By 1965, the surgical anatomy was thoroughly and widely understood, antibiotics were widely available and useful for treating postoperative infections, and other major complications had also become more manageable.
Society and culture[edit]
Notable individuals who have or have had a tracheotomy include Mika Häkkinen, Stephen Hawking, Connie Culp, Christopher Reeve,[50] Roy Horn, William Rehnquist, Gabby Giffords, George Michael, Val Kilmer,[51] and many others.[52]
Across movies and TV shows, there are many situations where an emergency procedure is done on an individual's neck to re-establish an airway. An example is in the 2008 horror film, Saw V, in which a character being drowned from the neck up performs a manual tracheotomy, stabbing his neck with a pen to create an airway to breathe through. The most common procedure is a cricothyrotomy (or "crike"), which is an incision through the skin and cricothyroid membrane. This is often confused or misnamed as a tracheotomy (or "trach") and vice versa. However, they are quite different based on location of the opening and length of time the alternate airway is needed.
References[edit]
- ^ Molnar, Heather (11 April 2023). "Types of Tracheostomy Tubes".
- ^ a b Romaine F. Johnson (6 March 2003). "Adult Tracheostomy". Houston, Texas: Department of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, Baylor College of Medicine. Archived from the original on 17 May 2008.
- ^ a b Jonathan P Lindman; Charles E Morgan (7 June 2010). "Tracheostomy". WebMD.
- ^ Eberhardt, Lars Karl (2008). Dilatational Tracheostomy on an Intensive Care Unit (Dissertation). Universität Ulm.
- ^ Esteban A, Anzueto A, Alía I, Gordo F, Apezteguía C, Pálizas F, Cide D, Goldwaser R, Soto L, Bugedo G, Rodrigo C, Pimentel J, Raimondi G, Tobin MJ (May 2000). "How is mechanical ventilation employed in the intensive care unit? An international utilization review". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 161 (5): 1450–8. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.161.5.9902018. PMID 10806138.
- ^ Linton, DM (2005). "Cuirass ventilation: a review and update". Critical Care and Resuscitation. 7 (1): 22–8. doi:10.1016/S1441-2772(23)01566-1. PMID 16548815.
- ^ Taylor, C. R., Lillis, C., LeMone, P., Lynn, P. (2011) Fundamentals of nursing: The art and science of nursing care. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, page 1382–1383, 1404.
- ^ Passy V, Baydur A, Prentice W, Darnell-Neal R (1993). "Passy-Muir tracheostomy speaking valve on ventilator-dependent patients". The Laryngoscope. 103 (6): 653–8. doi:10.1288/00005537-199306000-00013. PMID 8502098. S2CID 22397705.
- ^ Cullen JH (1963). "An evaluation of tracheostomy in pulmonary emphysema". Annals of Internal Medicine. 58 (6): 953–60. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-58-6-953. PMID 14024192.
- ^ a b Lalwani, Anil K. (2012). CURRENT Diagnosis & Treatment in Otolaryngology—Head & Neck Surgery, 3e. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. pp. Yu KY. Chapter 38. Airway Management & Tracheotomy. ISBN 978-0-07-162439-8.
- ^ a b Ellison, E. Christopher; Zollinger, Jr, Robert M. (2016). Zollinger's Atlas of Surgical Operations, 10th edition. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. pp. Chapter 120- Tracheotomy, Chapter 121- Tracheotomy, Percutaneous Dilational. ISBN 978-0-07-179755-9.
- ^ Ciaglia P, Firsching R, Syniec C (June 1985). "Elective percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy. A new simple bedside procedure; preliminary report". Chest. 87 (6): 715–9. doi:10.1378/chest.87.6.715. PMID 3996056. S2CID 27125996.
- ^ Griggs WM, Worthley LI, Gilligan JE, Thomas PD, Myburg JA (June 1990). "A simple percutaneous tracheostomy technique". Surgery, Gynecology & Obstetrics. 170 (6): 543–5. PMID 2343371.
- ^ "Translaryngeal Tracheostomy- TLT Fantoni method". www.translaryngealtracheostomyfantoni.it. Archived from the original on 11 September 2017. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- ^ a b Ambesh SP, Pandey CK, Srivastava S, Agarwal A, Singh DK (December 2002). "Percutaneous tracheostomy with single dilatation technique: a prospective, randomized comparison of Ciaglia blue rhino versus Griggs' guidewire dilating forceps". Anesthesia and Analgesia. 95 (6): 1739–45, table of contents. doi:10.1097/00000539-200212000-00050. PMID 12456450. S2CID 22222451.
- ^ Rosen H (January 1897). "On enactment". Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association. 40 (4): 1228–9. doi:10.1097/00000441-189701000-00008. PMC 1430766. PMID 1430766.
- ^ a b c d Ferlito A, Rinaldo A, Shaha AR, Bradley PJ (December 2003). "Percutaneous tracheotomy". Acta Oto-Laryngologica. 123 (9): 1008–12. doi:10.1080/00016480310000485. PMID 14710900. S2CID 23470798.
- ^ a b c d Simon M, Metschke M, Braune SA, Püschel K, Kluge S (October 2013). "Death after percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy: a systematic review and analysis of risk factors". Critical Care. 17 (5): R258. doi:10.1186/cc13085. PMC 4056379. PMID 24168826.
- ^ a b c Klemm E, Nowak AK (April 2017). "Tracheotomy-Related Deaths". Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. 114 (16): 273–279. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2017.0273. PMC 5437259. PMID 28502311.
- ^ Grant CA, Dempsey G, Harrison J, Jones T (January 2006). "Tracheo-innominate artery fistula after percutaneous tracheostomy: three case reports and a clinical review". British Journal of Anaesthesia. 96 (1): 127–31. doi:10.1093/bja/aei282. PMID 16299043.
- ^ Rajendram (2017). "Tracheostomy tube displacement: An update on emergency airway management". Indian Journal of Respiratory Care. 6 (2): 800–806. doi:10.4103/ijrc.ijrc_12_17.
- ^ a b Dempsey, Ged A.; Morton, Ben; Hammell, Clare; Williams, Lisa T.; Smith, Catrin Tudur; Jones, Terence (1 March 2016). "Long-term Outcome Following Tracheostomy in Critical Care: A Systematic Review*". Critical Care Medicine. 44 (3): 617–628. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000001382. ISSN 0090-3493. PMID 26584197. S2CID 32649464.
- ^ Añón JM, Gómez V, Escuela MP, De Paz V, Solana LF, De La Casa RM, Pérez JC, Zeballos E, Navarro L (2000). "Percutaneous tracheostomy: comparison of Ciaglia and Griggs techniques". Critical Care. 4 (2): 124–8. doi:10.1186/cc667. PMC 29040. PMID 11056749.
- ^ van Heurn LW, van Geffen GJ, Brink PR (July 1996). "Clinical experience with percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy: report of 150 cases". The European Journal of Surgery = Acta Chirurgica. 162 (7): 531–5. PMID 8874159.
- ^ Polderman KH, Spijkstra JJ, de Bree R, Christiaans HM, Gelissen HP, Wester JP, Girbes AR (May 2003). "Percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy in the ICU: optimal organization, low complication rates, and description of a new complication". Chest. 123 (5): 1595–602. doi:10.1378/chest.123.5.1595. PMID 12740279.
- ^ Hill BB, Zweng TN, Maley RH, Charash WE, Toursarkissian B, Kearney PA (August 1996). "Percutaneous dilational tracheostomy: report of 356 cases". The Journal of Trauma. 41 (2): 238–43, discussion 243–4. doi:10.1097/00005373-199608000-00007. PMID 8760530.
- ^ Powell DM, Price PD, Forrest LA (February 1998). "Review of percutaneous tracheostomy". The Laryngoscope. 108 (2): 170–7. doi:10.1097/00005537-199802000-00004. PMID 9473064. S2CID 44972690.
- ^ Hotchkiss KS, McCaffrey JC (January 2003). "Laryngotracheal injury after percutaneous dilational tracheostomy in cadaver specimens". The Laryngoscope. 113 (1): 16–20. doi:10.1097/00005537-200301000-00003. PMID 12514375. S2CID 25597029.
- ^ Byhahn C, Lischke V, Halbig S, Scheifler G, Westphal K (March 2000). "[Ciaglia blue rhino: a modified technique for percutaneous dilatation tracheostomy. Technique and early clinical results]" [Ciaglia blue rhino: a modified technique for percutaneous dilatation tracheostomy. Technique and early clinical results]. Der Anaesthesist (in German). 49 (3): 202–6. doi:10.1007/s001010050815. PMID 10788989. S2CID 42582829.
- ^ Steven E. Sittig; James E. Pringnitz (February 2001). "Tracheostomy: evolution of an airway" (PDF). AARC Times: 48–51. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 April 2017. Retrieved 5 June 2008.
- ^ Yapijakis, Christos (4 July 2009). "Hippocrates of Kos, the father of clinical medicine, and Asclepiades of Bithynia, the father of molecular medicine. Review". In Vivo (Athens, Greece). 23 (4): 507–514. PMID 19567383.
- ^ Myers, Eugene N. (2007). Tracheotomy: Airway Management, Communication, and Swallowing, Second Edition. Plural Publishing. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-59756-840-1.
- ^ Patricia Skinner (2008). "Unani-tibbi". In Fundukian LJ (ed.). The Gale Encyclopedia of Alternative Medicine (3rd ed.). Farmington Hills, Michigan: Gale Cengage. ISBN 978-1-4144-4872-5.
- ^ Mostafa Shehata (April 2003). "The Ear, Nose and Throat in Islamic Medicine" (PDF). Journal of the International Society for the History of Islamic Medicine. 2 (3): 2–5. ISSN 1303-667X.
- ^ a b Goodall, E.W. (1934). "The story of tracheostomy". British Journal of Children's Diseases. 31: 167–76, 253–72.
- ^ Sedvall G, Farde L, Nybäck H, Pauli S, Persson A, Savic I, Wiesel FA (1960). "Recent advances in psychiatric brain imaging". Acta Radiologica. Supplementum. 374 (5179): 113–5. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.5179.1129. PMC 1966956. PMID 1966956.
- ^ a b Nicholas Habicot (1620). Question chirurgicale par laquelle il est démonstré que le Chirurgien doit assurément practiquer l'operation de la Bronchotomie, vulgairement dicte Laryngotomie, ou perforation de la fluste ou du polmon (in French). Paris: Corrozet. p. 108.
- ^ Sanctorii Sanctorii (1646). Sanctorii Sanctorii Commentaria in primum fen, primi libri canonis Avicennæ (in Latin). Venetiis: Apud Marcum Antonium Brogiollum. p. 1120. OL 15197097M.
- ^ Julius Casserius (Giulio Casserio) and Daniel Bucretius (1632). Tabulae anatomicae LXXIIX ... Daniel Bucretius ... XX. que deerant supplevit & omnium explicationes addidit (in Latin). Francofurti: Impensis & coelo Matthaei Meriani.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Cawthorne T, Hewlett AB, Ranger D (June 1959). "Tracheostomy in a respiratory unit at a neurological hospital". Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine. 52 (6): 403–5. doi:10.1177/003591575905200602. PMC 1871130. PMID 13667911.
- ^ Georges Detharding (1745). "De methodo subveniendi submersis per laryngotomiam (1714)". In Von Ernst Ludwig Rathlef; Gabriel Wilhelm Goetten; Johann Christoph Strodtmann (eds.). Geschichte jetzlebender Gelehrten, als eine Fortsetzung des Jetzlebenden. Zelle: Berlegts Joachim Undreas Deek. p. 20.
- ^ Price JL (January 1962). "The evolution of breathing machines". Medical History. 6 (1): 67–72. doi:10.1017/s0025727300026867. PMC 1034674. PMID 14488739.
- ^ Wischhusen HG, Schumacher GH (1977). "[Curriculum vitae of the professor of anatomy, botany and higher mathematics Georg Detharding (1671–1747) at the University of Rostock (author's transl)]" [Curriculum vitae of the professor of anatomy, botany and higher mathematics Georg Detharding (1671–1747) at the University of Rostock]. Anatomischer Anzeiger (in German). 142 (1–2): 133–40. PMID 339777.
- ^ Armand Trousseau (1833). "Mémoire sur un cas de tracheotomie pratiquée dans la période extrème de croup". Journal des connaissances médico-chirurgicales. 1 (5): 41.
- ^ Armand Trousseau (1852). "Nouvelles recherches sur la trachéotomie pratiquée dans la période extrême du croup". In Jean Lequime and J. de Biefve (ed.). Annales de médecine belge et étrangère. Brussels: Imprimerie et Librairie Société Encyclographiques des Sciences Médicales. pp. 279–288.
- ^ Snow J (1858). "Fatal cases of inhalation of chloroform, Treatment of suspended animation from chloroform". In Richardson BW (ed.). On chloroform and other anaesthetics: their action and administration. London: John Churchill. pp. 120–200, 251–62.
john snow.
- ^ Trendelenburg, F (1871). "Beiträge zu den Operationen an den Luftwegen" [Contributions to airways surgery]. Archiv für Klinische Chirurgie (in German). 12: 112–33.
- ^ Macewen W (July 1880). "General Observations on the Introduction of Tracheal Tubes by the Mouth, Instead of Performing Tracheotomy or Laryngotomy". British Medical Journal. 2 (1021): 122–4. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.1021.122. PMC 2241154. PMID 20749630.
- ^ Macewen W (July 1880). "Clinical Observations on the Introduction of Tracheal Tubes by the Mouth, Instead of Performing Tracheotomy or Laryngotomy". British Medical Journal. 2 (1022): 163–5. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.1022.163. PMC 2241109. PMID 20749636.
- ^ "Biography (Christopher Reeve Homepage)". www.chrisreevehomepage.com. Retrieved 19 December 2018.
- ^ Day, Nate (3 August 2020). "Val Kilmer says he's doing great after tracheotomy: 'I feel a lot better than I sound'". Fox News. Retrieved 14 June 2022.
- ^ "Famous people who have or have had Tracheostomies". www.tracheostomy.com. Archived from the original on 24 December 2018. Retrieved 19 December 2018.
Further reading[edit]
- Plotnikow GA, Roux N, Feld V, Gogniat E, Villalba D, Ribero NV, Sartore M, Bosso M, Quiroga C, Leiva V, Scrigna M, Puchulu F, Distéfano E, Scapellato JL, Intile D, Planells F, Noval D, Buñirigo P, Jofré R, Nielsen ED (October 2013). "Evaluation of tracheal cuff pressure variation in spontaneously breathing patients". International Journal of Critical Illness and Injury Science. 3 (4): 262–8. doi:10.4103/2229-5151.124148. PMC 3891193. PMID 24459624.
External links[edit]
- Tracheotomy Info (A community for tracheotomy-wearers and the people who love them) at tracheotomy.info
- Tracheostomy Products and Support (Online resource for tracheostomy products, supplies and support) at trachs.com
- Aaron's tracheostomy page (Caring for a tracheostomy) at tracheostomy.com
- (Pictures with video clipping) at drtbalu.com
- Translaryngeal tracheostomy Archived 11 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- "Tracheotomy" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- Smiths Medical Tracheostomy Training Videos
- A Video of Rescue Breathing for Laryngectomees and Neck Breathers
- "Book of Simplification Concerning Therapeutics and Diet", is a manuscript from 1497 that discusses tracheotomies
- An all inclusive resource about tracheostomy including articles and courses for medical professionals, caregivers and patients
- Site and blog with information about tracheostomies
- Global Tracheostomy Collaborative. International collaborative with resources for hospitals, caregivers, and patients about tracheostomies, including international research
- Dilatational Tracheostomy On An Intensive Care Unit
