Visigothic script
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (November 2015) |
This article needs editing to comply with Wikipedia's Manual of Style. (November 2015) |
| Visigothic script littera mozarabica, littera toletana | |
|---|---|
 Alphabet in Visigothic script | |
| Script type | Alphabetic
|
Time period | 7th century to 13th century |
| Direction | Left to right |
| Region | Iberian Peninsula |
| Languages | Medieval Latin |
| Related scripts | |
Parent systems | |
Sister systems | Beneventan, Merovingian |
Visigothic script was a type of medieval script that originated in the Visigothic kingdom in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula). Its more limiting alternative designations littera toletana and littera mozarabica associate it with scriptoria specifically in Toledo and with Mozarabic culture more generally, respectively.
The script, which exists in book-hand and cursive versions, was used from approximately the late seventh century until the thirteenth century, mostly in Visigothic Iberia but also somewhat in the Catalan kingdom in current southern France. It was perfected in the 9th–11th centuries and declined afterwards. It developed from uncial script, and shares many features of uncial, especially an uncial form of the letter ⟨g⟩.
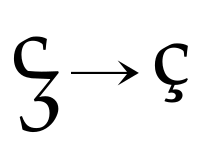
Other features of the script include an open-top ⟨a⟩ (very similar to the letter ⟨u⟩), similar shapes for the letters ⟨r⟩ and ⟨s⟩, and a long letter ⟨i⟩ resembling the modern letter ⟨l⟩. There are two forms of the letter ⟨d⟩, one with a straight vertical ascender and another with an ascender slanting towards the left. The top stroke of the letter ⟨t⟩, by itself, has a hook curving to the left; ⟨t⟩ also has a number of other forms when used in ligatures, and there are two different ligatures for the two sounds of ⟨ti⟩ (“hard” or unassibilated and "soft" or sibilated) as spoken in Hispano-Latin during this period. The letters ⟨e⟩ and ⟨r⟩ also have many different forms when written in ligature. Of particular interest is the special Visigothic z ⟨ꝣ⟩, which, after adoption into Carolingian handwriting, eventually transformed into the c-cedilla ⟨ç⟩.

From the standard script, a capital-letter display script was developed, with long slender forms. There was also a cursive form that was used for charters and non-religious writings, which had northern ("Leonese") and southern ("Mozarabic") forms. The Leonese cursive was used in the Christian north, and the Mozarabic was used by Christians living in the Muslim south. The cursive forms were probably influenced by Roman cursive, brought to Iberia from North Africa.
Visigothic script has many similarities with Beneventan script and Merovingian script.
| Preview | Ꝣ | ꝣ | Ç | ç | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER VISIGOTHIC Z | LATIN SMALL LETTER VISIGOTHIC Z | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER C WITH CEDILLA | LATIN SMALL LETTER C WITH CEDILLA | ||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 42850 | U+A762 | 42851 | U+A763 | 199 | U+00C7 | 231 | U+00E7 |
| UTF-8 | 234 157 162 | EA 9D A2 | 234 157 163 | EA 9D A3 | 195 135 | C3 87 | 195 167 | C3 A7 |
| Numeric character reference | Ꝣ |
Ꝣ |
ꝣ |
ꝣ |
Ç |
Ç |
ç |
ç |
| Named character reference | Ç | ç | ||||||
See also[edit]
Further reading[edit]
- 'Fonts for Latin Paleography: User's Manual. 6th edition' A manual of Latin paleography; a comprehensive PDF file containing 82 pages profusely illustrated, 4 January 2024).
- Littera Visigothica, blog specialized in Visigothic script
- Visigothic Minuscule on Medieval Writing
- Muñoz y Rivero, Jesús (1919). Paleografía visigoda: método teórico-práctico para aprender a leer los códices y documentos españoles de los siglos V al XII; obra ilustrada con 45 láminas dibujadas por el autor (Visigothic Paleography: A Theoretical-Practical Method for Learning to Read Spanish Codices and Documents from the 5th to 11th centuries; Illustrated with 45 Figures Drawn by the Author) (in Spanish). Madrid: D. Jorro.
- Alturo Perucho, Jesús (2004). "La escritura visigótica. Estado de la cuestión". Archiv für Diplomatik (in Spanish) (50). Viena: 347–386. ISSN 0066-6297.
- Castro Correa, Ainoa (2020). "Leaving the Past behind, Adapting to the Future: Transitional and Polygraphic Visigothic-Caroline Minuscule Scribes". Anuario de Estudios Medievales. 50 (2): 631–664. doi:10.3989/AEM.2020.50.2.01.
- Castro Correa, Ainoa (2021). "Dating and placing Visigothic script codices: A quick guide for beginners". Le livre et l'écrit: Le manuscrit médiéval: Texte, objet et outil de transmission (2): 7–35.
- del Camino Martínez, Mª del Carmen (1990). Los orígenes de la escritura visigótica (in Spanish). Madrid-Toledo. pp. 29–37. ISBN 84-7094-111-9.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Díaz y Díaz, Manuel (1979). Libros y librerías en la Rioja altomedieval (in Spanish). Logroño: IER.
- Díaz y Díaz, Manuel (1983). Códices visigóticos en la Monarquía leonesa. León: CSIC.
- Millares Carlo, Agustín (1973). Consideraciones sobre la escritura visigótica cursiva. León.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Millares Carlo, Agustín; con la colaboración de José Manuel Ruiz Asencio (1983). Tratado de Paleografía Española (in Spanish). Madrid: Espasa Calpe. ISBN 84-239-4986-9.
- Mundó, Anscari M. (1965). "La datación de los códices litúrgicos toledanos". Hispania Sacra (in Spanish). XVIII. ISSN 0018-215X.
- Mundó, Anscari M.; Alturo Perucho, Jesús (1990). "La escritura de transición de la visgótica a la carolina en la Cataluña del siglo IX". Actas del VIII Coloquio del Comité International de Paléographie Latine (in Spanish). Madrid-Toledo: 131–138. ISBN 84-7094-111-9.
- Núñez Contreras, Luis (1994). Manual de Paleografía (in Spanish). Madrid: Cátedra. ISBN 84-376-1245-4.
- Rodríguez Díaz, Elena E. (2011). Die Mozaraber. Definitionen und Perspektiven der Forschung [Los manuscritos mozárabes: una encrucijada de culturas] (in German). Münster: Lit. ISBN 978-3-643-11117-3.
- Selig, Maria; Frank, Barbara; Hartmann, Jörg (1993). Le passage à l'écrit des langues romanes (in French). Gunter Narr Verlag. ISBN 9783823342618.
- Velázquez Soriano, Isabel (1989). Las pizarras visigodas. Edición crítica y estudio. Antigüedad y Cristianismo: Monografías históricas sobre la Antigüedad Tardía (in Spanish). Murcia: Universidad de Murcia. ISSN 0214-7165.

