Skjöldr
| Skjöldr | |
|---|---|
| King of the Danes | |
| Predecessor | Odin |
| Successor | Gram |
| Consort | Alfhild |
| Issue | Gram |
| House | Scylding |
| Father | Odin |
| Religion | Germanic paganism |
| Characters of Gesta Danorum |
|---|
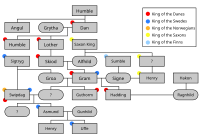 |
| Danish kings |
| Foreign rulers |
| Other men |
| Women |
Skjöldr (Old Norse Skjǫldr, Icelandic Skjöldur, sometimes Anglicized as Skjold or Skiold, Latinized as Skioldus; Old English Scyld, Proto-Germanic *Skelduz ‘shield’) was among the first legendary Danish kings. He is mentioned in the Prose Edda, in Ynglinga saga, in Chronicon Lethrense, in Sven Aggesen's history, in Arngrímur Jónsson's Latin abstract of the lost Skjöldunga saga and in Saxo Grammaticus' Gesta Danorum. He also appears in the Old English poem Beowulf. The various accounts have little in common.
Primary sources[edit]
Beowulf[edit]
Skjǫldr appears in the prologue of Beowulf, where he is referred to as Scyld Scefing, implying he is a descendant or son of a Scef (‘Sheaf’, usually identified with Sceafa), or, literally, 'of the sheaf'. According to Beowulf he was found in a boat as a child, possibly an orphan, but grew on to become a powerful warrior and king:
Scyld the Sheaf-Child from scourging foemen,
From raiders a-many their mead-halls wrested.
He lives to be feared, the first has a waif,
Puny and frail he was found on the shore.
He grew to be great, and was girt with power
Till the border-tribes all obeyed his rule,
And sea-folk hardy that sit by the whale-path
Gave him tribute, a good king was he.[1]
After relating in general terms the glories of Scyld's reign, the poet describes Scyld's funeral, his body was laid in a ship surrounded by treasures:
They decked his body no less bountifully
with offerings than those first ones did
who cast him away when he was a child
and launched him alone out over the waves.
In line 33 of Beowulf, Scyld's ship is called īsig, literally, ‘icy.’ The meaning of this epithet has been discussed many times. Anatoly Liberman gives a full survey of the literature and suggests that the word meant "shining."[2]
William of Malmesbury's 12th century Chronicle tells the story of Sceafa as a sleeping child in a boat without oars with a sheaf of corn at his head.[3]
Olrik (1910) suggested Peko, a parallel "barley-figure" in Finnish, in turn connected by Fulk (1989) with Eddaic Bergelmir.[4]
[edit]
Legendary sagas[edit]
In the Ynglinga saga and in the now-lost Skjöldunga saga, Odin came from Asia (Scythia) and conquered Northern Europe. He gave Sweden to his son Yngvi and Denmark to his son Skjöldr. Since then the kings of Sweden were called Ynglings and those of Denmark Skjöldungs.
Gesta Danorum[edit]
In Gesta Danorum, Skioldus is the son of Lotherus, a wicked king who met his end in an insurrection.
References[edit]
- ^ McCallum, James Dow (1929). The Beginnings to 1500. New York, NY: Charles Scribner's Sons. p. 1.
- ^ Liberman, Anatoly (2016). In Prayer and Laughter. Essays on Medieval Scandinavian and Germanic Mythology, Literature, and Culture. Paleograph Press. pp. 270–278. ISBN 9785895260272.
- ^ Owen-Crocker, Gale R. (2000). The Four Funerals in Beowulf. Manchester, UK: Manchester University Press.
- ^ Fulk, R.D. (1989). "An eddic analogue to the Scyld Scefing story". The Review of English Studies (159): 313–322. doi:10.1093/res/XL.159.313.
- Davidson, Hilda Ellis, ed. (1999) [1979-1980 (first pub.)]. Saxo Grammaticus: The History of the Danes: Books I-IX. Translated by Fisher, Peter. Bury St Edmunds: St Edmundsbury Press. ISBN 0-85991-502-6.
- The Nine Books of the Danish History of Saxo Grammaticus. Translated by Elton, Oliver. New York, NY: Norroena Society. 1905.
- Olrik, J.; Ræder, H. (1931). Saxo Grammaticus: Gesta Danorum.
