RR Lyrae
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Lyra |
| Right ascension | 19h 25m 27.91285s[1] |
| Declination | +42° 47′ 03.6942″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 7.195[2] (7.06–8.12)[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A7III - F8III |
| U−B color index | +0.172[2] |
| B−V color index | +0.181[2] |
| Variable type | RR Lyr[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | -72.4[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: -109.68[1] mas/yr Dec.: -195.75[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.64 ± 0.23 mas[6] |
| Distance | 900 ± 60 ly (270 ± 20 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 0.600 ± 0.126[7] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.65[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 5.1 to 5.6[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 49 ± 5[8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 2.4 ± 0.2[8] cgs |
| Temperature | 6,125 ± 50[8] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | –1.16[7] dex |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
RR Lyrae is a variable star in the Lyra constellation, figuring in its west near to Cygnus.[10] As the brightest star in its class,[11] it became the eponym for the RR Lyrae variable class of stars[3] and it has been extensively studied by astronomers.[7] RR Lyrae variables serve as important standard candles that are used to measure astronomical distances. The period of pulsation of an RR Lyrae variable depends on its mass, luminosity and temperature, while the difference between the measured luminosity and the actual luminosity allows its distance to be determined via the inverse-square law. Hence, understanding the period-luminosity relation for a local set of such stars allows the distance of more distant stars of this type to be determined.[12]
History[edit]
The variable nature of RR Lyrae was discovered by the Scottish astronomer Williamina Fleming at Harvard Observatory in 1901.[10]
The distance of RR Lyrae remained uncertain until 2002 when the Hubble Space Telescope's fine guidance sensor was used to determine the distance of RR Lyrae within a 5% margin of error, yielding a value of 262 parsecs (855 light-years).[13] When combined with measurements from the Hipparcos satellite and other sources, the result is a distance estimate of 258 pc (841 ly).
Variable star class[edit]

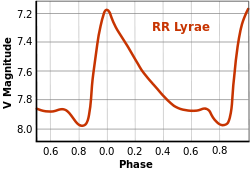
This type of low-mass star has consumed the hydrogen at its core, evolved away from the main sequence, and passed through the red giant stage. Energy is now being produced by the thermonuclear fusion of helium at its core, and the star has entered an evolutionary stage called the horizontal branch (HB). The effective temperature of an HB star's outer envelope will gradually increase over time. When its resulting stellar classification enters a range known as the instability strip—typically at stellar class A—the outer envelope can begin to pulsate.[12] RR Lyrae shows just such a regular pattern of pulsation, which is causing its apparent magnitude to vary between 7.06 and 8.12 over a short cycle lasting 0.56686776 days (13 hours, 36 minutes).[3] Each radial pulsation causes the radius of the star to vary between 5.1 and 5.6 times the Sun's radius.[8]
This star belongs to a subset of RR Lyrae-type variables that show a characteristic behavior called the Blazhko effect,[14] named after Russian astronomer Sergey Blazhko. This effect is observed as a periodic modulation of a variable star's pulsation strength or phase; sometimes both. It causes the light curve of RR Lyrae to change from cycle to cycle. In 2014, Time-series photometric observations demonstrated the physical origin of this effect.[15]
Other stellar classifications[edit]
As with other RR Lyrae-type variables, RR Lyrae itself has a low abundance of elements other than hydrogen and helium – what astronomers term its metallicity: It belongs to the Population II category of stars that formed during the early period of the Universe when there was a lower abundance of metals in star-forming regions.[16]
The trajectory of this star is carrying it along an orbit that is close to the plane of the Milky Way, taking it no more than 680 ly (210 pc) above or below this plane. The Blazhko period for RR Lyrae is 39.1 ± 0.3 days.[3] The orbit has a high eccentricity, bringing RR Lyrae as close as 6.80 kly (2.08 kpc) to the Galactic Center at periapsis, and taking it as far as 59.9 kly (18.4 kpc) at apapsis.[17]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600
- ^ a b c Schoeneich, W.; Lange, D. (1979), "UBV observations of RR Lyr", Information Bulletin on Variable Stars, 1557: 1–2, Bibcode:1979IBVS.1557....1S
- ^ a b c d Kolenberg, K.; et al. (February 2011), "Kepler photometry of the prototypical Blazhko star RR Lyr: an old friend seen in a new light", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 411 (2): 878–890, arXiv:1011.5908, Bibcode:2011MNRAS.411..878K, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17728.x, S2CID 73597094
- ^ Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009), "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)", VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S, 1, Bibcode:2009yCat....102025S
- ^ Wilson, Ralph Elmer (1953), "General Catalogue of Stellar Radial Velocities", Carnegie Institute Washington D.C. Publication, Washington: Carnegie Institution of Washington, Bibcode:1953GCRV..C......0W
- ^ Brown, A.G.A.; et al. (Gaia Collaboration) (November 2016), "Gaia Data Release 1. Summary of the astrometric, photometric, and survey properties", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 595 (A): 2, arXiv:1609.04172v1, Bibcode:2016A&A...595A...2G, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201629512, S2CID 1828208
- ^ a b c Catelan, M.; Cortés, C. (April 2008), "Evidence for an Overluminosity of the Variable Star RR Lyrae, and a Revised Distance to the LMC", The Astrophysical Journal, 676 (2): L135–L138, arXiv:0802.2063, Bibcode:2008ApJ...676L.135C, doi:10.1086/587515, S2CID 17268929
- ^ a b c d e f Kolenberg, K.; et al. (September 2010), "An in-depth spectroscopic analysis of the Blazhko star RR Lyrae. I. Characterisation of the star: abundance analysis and fundamental parameters" (PDF), Astronomy and Astrophysics, 519: A64, arXiv:1004.5156, Bibcode:2010A&A...519A..64K, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014471, S2CID 6401091[permanent dead link]
- ^ "V* RR Lyr -- Variable Star of RR Lyr type", SIMBAD, Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg, retrieved 2012-01-08
- ^ a b Burnham, Robert Jr. (1978), Burnham's Celestial Handbook, vol. 2, New York: Dover Publications, ISBN 0-486-23568-8
- ^ Templeton, Matthew (September 24, 2010), RR Lyrae, American Association of Variable Star Observers, retrieved 2012-01-08
- ^ a b Salaris, Maurizio; Cassisi, Santi (2005), Evolution of stars and stellar populations, John Wiley and Sons, pp. 181–182, ISBN 0-470-09220-3
- ^ Benedict, G. Fritz; et al. (January 2002), "Astrometry with the Hubble Space Telescope: A Parallax of the Fundamental Distance Calibrator RR Lyrae", The Astronomical Journal, 123 (1): 473–484, arXiv:astro-ph/0110271, Bibcode:2002AJ....123..473B, doi:10.1086/338087, S2CID 59150013
- ^ Smith, Horace A.; et al. (January 2003), "The Blazhko Effect of RR Lyrae in 1996", The Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 115 (803): 43–48, Bibcode:2003PASP..115...43S, doi:10.1086/345458
- ^ Chadid, M. (2014), "First Detection of Multi-shocks in RR Lyrae Stars from Antarctica: A Possible Explanation of the Blazhko Effect", The Astronomical Journal, 148 (5): 88–94, Bibcode:2014AJ....148...88C, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/148/5/88, S2CID 121252232
- ^ Inglis, Mike (2003), Observer's guide to stellar evolution: the birth, life, and death of stars, Patrick Moore's practical astronomy series, Springer, p. 162, ISBN 1-85233-465-7
- ^ Maintz, G.; de Boer, K. S. (October 2005), "RR Lyrae stars: kinematics, orbits and z-distribution", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 442 (1): 229–237, arXiv:astro-ph/0507604, Bibcode:2005A&A...442..229M, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053231, S2CID 54194736
External links[edit]
- Kaler, James B., "RR LYR (RR Lyrae)", Stars, University of Illinois, retrieved 2012-01-08
- Kaler, James B. (2002), The hundred greatest stars, Copernicus Series, Springer, p. 163, ISBN 0-387-95436-8
- image RR Lyrae