Prototile
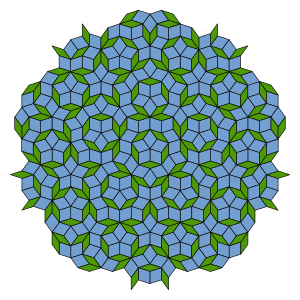
In mathematics, a prototile is one of the shapes of a tile in a tessellation.[1]
Definition[edit]
A tessellation of the plane or of any other space is a cover of the space by closed shapes, called tiles, that have disjoint interiors. Some of the tiles may be congruent to one or more others. If S is the set of tiles in a tessellation, a set R of shapes is called a set of prototiles if no two shapes in R are congruent to each other, and every tile in S is congruent to one of the shapes in R.[2]
It is possible to choose many different sets of prototiles for a tiling: translating or rotating any one of the prototiles produces another valid set of prototiles. However, every set of prototiles has the same cardinality, so the number of prototiles is well defined. A tessellation is said to be monohedral if it has exactly one prototile.
Aperiodicity[edit]

A set of prototiles is said to be aperiodic if every tiling with those prototiles is an aperiodic tiling. In March 2023, four researchers, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, David Smith, Joseph Samuel Myers and Craig S. Kaplan, announced the discovery of an aperiodic monohedral prototile (monotile) and a proof that the tile discovered by David Smith is an aperiodic monotile, i.e. a solution to a longstanding open einstein problem.[3][4]
In higher dimensions, the problem had been solved earlier: the Schmitt-Conway-Danzer tile is the prototile of a monohedral aperiodic tiling of three-dimensional Euclidean space, and cannot tile space periodically.
References[edit]
- ^ Cederberg, Judith N. (2001), A Course in Modern Geometries, Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics (2nd ed.), Springer-Verlag, p. 174, ISBN 978-0-387-98972-3.
- ^ Kaplan, Craig S. (2009), Introductory Tiling Theory for Computer Graphics, Synthesis Lectures on Computer Graphics and Animation, Morgan & Claypool Publishers, p. 7, ISBN 978-1-60845-017-6.
- ^ Roberts, Siobhan (2023-03-28). "Elusive 'Einstein' Solves a Longstanding Math Problem". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2023-06-02.
- ^ Smith, David; Joseph Samuel Myers; Kaplan, Craig S.; Goodman-Strauss, Chaim (2023). "An aperiodic monotile". arXiv:2303.10798 [math.CO].


