Pharyngeal nerve
| Pharyngeal nerve | |
|---|---|
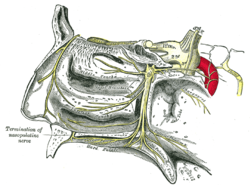 The pterygopalatine ganglion and its branches. (Pharyngeal visible at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| From | pterygopalatine ganglion |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus pharyngeus |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.044 |
| TA2 | 6223 |
| FMA | 77524 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The pharyngeal nerve is a small[citation needed] branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2),[1]: 496 arising at (the posterior part of the[citation needed]) pterygopalatine ganglion. It passes posterior-ward through the palatovaginal canal[1]: 370, 496 with the pharyngeal branch of the maxillary artery.[1]: 508
It is distributed to the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx[1]: 370, 496 (its posterior wall, posterior to the pharyngotympanic tube).[citation needed] It also issues some minute orbital branches which pass through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit and innervate the periosteum of the floor of the orbit, and the mucosa of the sphenoid sinus and ethmoid sinus.[1]: 370
See also[edit]
References[edit]
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 893 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 893 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links[edit]
