Obturator artery
| Obturator artery | |
|---|---|
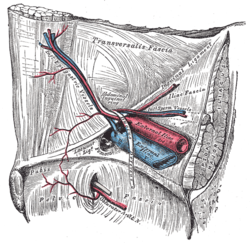 The relations of the femoral and abdominal inguinal rings, seen from within the abdomen. Right side. (Obturator artery is visible at bottom.) | |
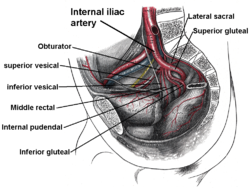 Internal iliac artery and some branches. | |
| Details | |
| Source | Internal iliac artery |
| Branches | anterior branch and posterior branch |
| Vein | Obturator veins |
| Supplies | Obturator externus muscle, medial compartment of thigh, femur |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria obturatoria |
| TA98 | A12.2.15.008 |
| TA2 | 4323 |
| FMA | 18865 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The obturator artery is a branch of the internal iliac artery that passes antero-inferiorly (forwards and downwards) on the lateral wall of the pelvis, to the upper part of the obturator foramen, and, escaping from the pelvic cavity through the obturator canal, it divides into an anterior branch and a posterior branch.
Structure[edit]
In the pelvic cavity this vessel is in relation, laterally, with the obturator fascia; medially, with the ureter, ductus deferens, and peritoneum; while a little below it is the obturator nerve.
The obturator artery usually arises from the internal iliac artery.[1][2] Inside the pelvis the obturator artery gives off iliac branches to the iliac fossa, which supply the bone and the Iliacus, and anastomose with the ilio-lumbar artery; a vesical branch, which runs backward to supply the bladder; and a pubic branch, which is given off from the vessel just before it leaves the pelvic cavity.
The pubic branch ascends upon the back of the pubis, communicating with the corresponding vessel of the opposite side, and with the inferior epigastric artery.
After passing through the obturator canal and outside of the pelvis, the obturator artery divides at the upper margin of the obturator foramen, into an anterior branch and a posterior branch of the obturator artery which encircle the foramen under cover of the obturator externus.
Anterior branch[edit]
The anterior branch of the obturator artery is a small artery in the thigh and runs forward on the outer surface of the obturator membrane and then curves downward along the anterior margin of the obturator foramen.
It distributes branches to the obturator externus, pectineus, adductors, and gracilis muscle, and anastomoses with the posterior branch and with the medial femoral circumflex artery.
Posterior branch[edit]
The posterior branch of the obturator artery is a small artery in the thigh and follows the posterior margin of the foramen and turns forward on the inferior ramus of the ischium, where it anastomoses with the anterior branch.
It gives twigs to the muscles attached to the ischial tuberosity and anastomoses with the inferior gluteal artery. It also supplies an articular branch which enters the hip-joint through the acetabular notch, ramifies in the fat at the bottom of the acetabulum and sends a twig along the ligament of head of femur (ligamentum teres) to the head of the femur.
The blood supply to the femoral head and neck is enhanced by the artery of the ligamentum teres derived from the obturator artery. In adults, this is small and doesn't have much importance, but in children whose epiphyseal line is still made of cartilage (which doesn't allow blood supply through it), it helps to supply the head and neck of the femur on its own.
The articular branch is usually patent until roughly 15 years of age. In adults it does not provide enough blood supply to prevent avascular necrosis in upper femur fractures.
Variation[edit]

The obturator artery usually arises from the main stem or from the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery.[1][2] It may arise from the superior gluteal artery, and occasionally it arises from the external iliac.
In about two out of every seven cases it arises from the inferior epigastric and descends almost vertically to the upper part of the obturator foramen. In studies, it has been found that corona mortis is in half of all hemipelvis with a prevalence of 46%.[3] In other studies, it is found to be 33.33% in both hemipelves of the individuals.[4] The variation has also been found to be more common in patients from Europe than in Asia where studies have been conducted. In comparative studies, it was found that European patients had a 10% higher chance of having the arterial variation when compared to Asian population.[5] The artery in this course usually lies in contact with the external iliac vein, and on the lateral side of the femoral ring (Figure A on diagram). It can also pass medial to the femoral ring along the margin of the lacunar ligament (Figure B). In either case it would be at risk of injury during the operation to repair a femoral hernia, whether the hernia is reducible, incarcerated or strangulated. When the obturator artery travels along the lacunar ligament, it nearly encircles the femoral ring and can be lacerated during a femoral hernia repair. Most femoral hernias are repaired through a small (1/2 to 3/4 inch) incision in the groin area, rather than through the abdomen, so if a laceration were to occur, bleeding may not be immediately recognized and result in significant blood loss into the peritoneal cavity. Because of this danger, the anatomic variant in Figure B is sometimes referred to as the "crown of death" (corona mortis).[6][7]
Additional images[edit]
-
Right hip bone. Internal surface.
-
Left levator ani from within.
References[edit]
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 616 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 616 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b Kumari, Savita; Trinesh Gowda, M. S. (2016-08-01). "A study of variations of origin of obturator artery: Review in south Indian population". Journal of the Anatomical Society of India. 65: S1–S4. doi:10.1016/j.jasi.2016.05.001. ISSN 0003-2778.
- ^ a b Biswas, Sharmishta; Bandopadhyay, Manimay; Adhikari, Anjan; Kundu, Panchanan; Roy, Rita (2010-12-01). "Variation of Origin of Obturator Artery in Eastern Indian Population - A Study". Journal of Anatomical Society of India. 59 (2): 168–172. doi:10.1016/S0003-2778(10)80019-X. ISSN 0003-2778.
- ^ Noussios, George; Galanis, Nikiforos; Chatzis, Iosif; Konstantinidis, Sergios; Filo, Eva; Karavasilis, George; Katsourakis, Anastasios (2020). "The Anatomical Characteristics of Corona Mortis: A Systematic Review of the Literature and Its Clinical Importance in Hernia Repair". Journal of Clinical Medicine Research. 12 (2): 108–114. doi:10.14740/jocmr4062. ISSN 1918-3003. PMC 7011932. PMID 32095180.
- ^ Heichinger, René; Pretterklieber, Michael L.; Hammer, Niels; Pretterklieber, Bettina (January 2023). "The Corona mortis is similar in size to the regular obturator artery, but is highly variable at the level of origin: an anatomical study". Anatomical Science International. 98 (1): 43–53. doi:10.1007/s12565-022-00671-w. ISSN 1447-6959. PMC 9845159. PMID 35653059.
- ^ Noussios, George; Galanis, Nikiforos; Chatzis, Iosif; Konstantinidis, Sergios; Filo, Eva; Karavasilis, George; Katsourakis, Anastasios (2020). "The Anatomical Characteristics of Corona Mortis: A Systematic Review of the Literature and Its Clinical Importance in Hernia Repair". Journal of Clinical Medicine Research. 12 (2): 108–114. doi:10.14740/jocmr4062. ISSN 1918-3003. PMC 7011932. PMID 32095180.
- ^ "Corona Mortis". Medical Terminology Daily. Clinical Anatomy Associates, Inc. 4 December 2012. Retrieved 6 October 2013.
- ^ Rusu, Mugurel Constantin; Cergan, Romica; Motoc, Andrei Gheorghe Marius; Folescu, Roxana; Pop, Elena (28 July 2009). "Anatomical considerations on the corona mortis". Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy. 32 (1): 17–24. doi:10.1007/s00276-009-0534-7. PMID 19636491. S2CID 25637954.
External links[edit]
- Anatomy photo:43:13-0201 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Pelvis: Branches of Internal Iliac Artery"
- pelvis at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (pelvicarteries)
- MedEd at Loyola Grossanatomy/dissector/practical/pelvis/pelvis15.html
- Variations at anatomyatlases.org
- Variations at anatomyatlases.org