Nereus (underwater vehicle)
 Nereus
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | Nereus |
| Owner | Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) |
| Operator | WHOI |
| Builder | WHOI |
| Acquired | 1995 |
| Commissioned | 2009 |
| In service | 2009~2014 |
| Homeport | Woods Hole, Massachusetts, United States |
| Fate | Imploded due to high pressure in Kermadec Trench 10 May 2014 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type | remotely operated underwater vehicle |
| Tonnage | 2,800 kilograms (6,200 lb) |
| Length | 3 metres (9.8 ft) |
| Installed power | electrical (rechargeable Lithium-ion batteries) |
| Speed | 3 knots |
| Test depth | 10,902 metres (35,768 ft) |
| Complement | unmanned |
| Sensors and processing systems | side-scan sonar & LED search lights |
Nereus was a hybrid uncrewed autonomous underwater vehicle (HROV, a type of remotely operated underwater vehicle) built by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI). Constructed as a research vehicle to operate at depths of up to 11,000 metres (36,000 ft), it was designed to explore Challenger Deep, the deepest surveyed point in the global ocean. Nereus, named for Greek sea titan Nereus (who has a man's torso and a fish-tail) through a nationwide contest of high school and college students, began its deep sea voyage to Challenger Deep in May 2009 and reached the bottom on May 31, 2009.[1][2]
On this dive the Nereus reached a depth of 35,768 feet (10,902 m), making the Nereus the world's deepest-diving vehicle in operation at the time, and the first since 1998 to explore the Mariana Trench, the deepest known part of the ocean.[2][3]
On 10 May 2014, Nereus was lost while exploring the Kermadec Trench at a depth of 9,900 metres (32,500 ft). Communications were cut off at around 2 p.m. local time, and debris retrieved later revealed that it imploded due to high pressure.
Hybrid design[edit]
Being a hybrid ROV means that the vehicle could operate untethered or tethered with a thin optical fiber cable and operated by pilots aboard the ship. The latter enabled it to make deep dives while being highly maneuverable.[3] The optical fiber tether has the approximate diameter of a human hair, and can bear only 4 kilograms (8.8 lb). It is made up of a thin layer of plastic surrounding a slender glass fiber core. The vehicle carried approximately 40 kilometers (25 mi) of cable wound in two small canisters that pay out the fiber as the vehicle descends. This slim tether is smaller, lighter, and more cost-effective than cable.[3]
Nereus weighed approximately 3 tons and was about 4.25 meters (14 feet) long and 2.3 meters (8 feet) wide. Approximately 2,000 lithium-ion batteries provided its power. The vehicle made use of precisely designed ceramic spheres rather than the much heavier syntactic foam that is typically used for submersible vehicles. Each hull contained between 700 and 800 9-cm (3.5-inch) hollow spheres that were specifically designed to handle intense pressure. Nereus had a lightweight robotic manipulator arm to conduct the sample collecting that operates hydraulically and was able to perform under intense pressure.[4]
As an alternative to the tether, the Nereus could be switched to a free-swimming mode and operated as an autonomous vehicle to survey the ocean floor.[3]
In designing the vehicle, the design team led by Andy Bowen at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution relied on previous experience in developing autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) and tethered robots to build a hybrid ROV that could both fly like an aircraft to explore large areas of the ocean floor, but would be easily converted to able to hover over the small areas to conduct experiments or collect samples of rocks and sea life.[4]
Deepest dive[edit]
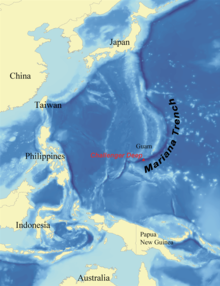
The Challenger Deep is located in the Western Pacific Ocean near the island of Guam in the Mariana Trench, the deepest known part of an ocean on Earth, and the deepest known location on Earth.[5] The May 2009 dive by the Nereus achieved a depth of 10,902 metres (35,768 ft), making it the world's deepest-diving vehicle then in operation, and the first since 1998 to explore the Mariana Trench.[3] To accomplish this dive, the vehicle had to sustain pressures over 1,000 times the atmospheric pressure at the Earth's surface.[4] It hovered over the trench for more than 10 hours and sent back live video to the mother ship.[2]
Nereus is the third vehicle in the world to reach the bottom of the Pacific Ocean's Challenger Deep. The first was the crewed Bathyscaphe Trieste, which carried U.S. Navy Lieutenant Don Walsh and Swiss engineer Jacques Piccard and made the voyage on 23 January 1960. The Nereus dive aimed for the same spot. On 24 March 1995 a Japanese robotic deep-sea probe called Kaikō made the first uncrewed trip to the Challenger Deep.[6]
Once at the bottom, Nereus collected liquid and rock specimens. Patricia Fryer, co-chief scientist of the expedition, said the following about the samples.
"We want to know how all of this relates to subduction around the globe, changes in the chemistry of the ocean in general and, therefore, potential effects those changes may have on ocean-atmosphere interactions and things like global climate change."[7]
Loss[edit]
On 10 May 2014, at around 2 p.m. local time, Nereus was lost while conducting a dive at 9,900 metres (32,500 ft) in depth in the Kermadec Trench, believed to be caused by extreme pressure at up to 110 megapascals (16,000 psi).[8]
Nereus was sent to complete the first systematic study of a deep-ocean trench as part of the NSF-sponsored Hadal Ecosystems Study (HADES) project under chief scientist Timothy Shank, a WHOI biologist who also helped conceive the vehicle. It was being controlled from the Research Vessel Thomas G. Thompson. Thirty days into the forty-day mission, about seven hours into a nine-hour dive, communications with Nereus were lost. When standard emergency recovery protocols were unsuccessful, the team initiated a search near the dive site. They then spotted several pieces of debris on the surface nearby later identified to be parts of Nereus, indicating a catastrophic implosion. The ship's crew recovered the debris to confirm its identity and to discover more information about the nature of the failure. Despite this, WHOI Director of Research Larry Madin stated that WHOI will continue to develop, build, and operate more underwater research craft for oceanographic exploration.[9]
References[edit]
- ^ Harlow, John (22 February 2009). "Old rivalries surface as US races to sea's deepest spot". London: The Sunday Times UK. Retrieved 2009-02-22.
- ^ a b c "Robot sub reaches deepest ocean". BBC News. 2009-06-03. Retrieved 2009-06-11.
- ^ a b c d e "Hybrid remotely operated vehicle 'Nereus' reaches deepest part of the ocean". www.physorg.com. Retrieved 2009-06-11.
- ^ a b c "Exploring the Deepest Part of the Ocean - Mariana Trench". geology.com. Retrieved 2009-06-11.
- ^ "The Mariana Trench". www.marianatrench.com. Archived from the original on 2009-04-03. Retrieved 2009-06-11.
- ^ Hadfield, Peter (2 November 1996). "Mission to Marianas - If Mount Everest was dropped into the world's deepest trench, it would drown. Kaiko hit bottom . . . and came back to tell the tale". New Scientist. Retrieved 2023-09-26.
- ^ Altonn, Helen. "Robot sub helps collect deep-ocean specimens". Star-Bulletin. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
- ^ Haven Orecchio-Egresitz (May 10, 2014). "WHOI research sub goes missing in New Zealand". Cape Cod Times. Archived from the original on May 12, 2014. Retrieved May 10, 2014.
- ^ "Robotic Deep-sea Vehicle Lost on Dive to 6-Mile Depth". WHOI. May 10, 2014. Retrieved May 10, 2014.
