Klarälven
| Klarälven | |
|---|---|
 Sola i Karlstad statue | |
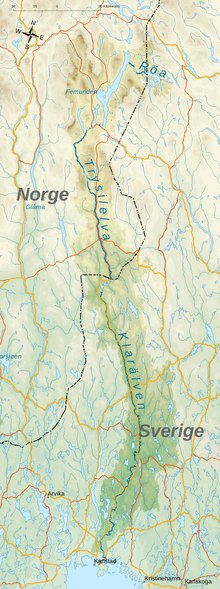 Topographic map of Klarälven river, where the area for the drainage basin for Klarälven is highlighted. | |
| Location | |
| Country | Sweden, Norway |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Rogen and Femund |
| Mouth | Vänern |
• location | Karlstad |
• coordinates | 59°23′19″N 13°29′54″E / 59.38861°N 13.49833°E |
• elevation | 44 m (144 ft) |
| Length | 460 km (290 mi)[1] |
| Basin size | 11,820 km2 (4,560 sq mi)[1] |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 165 m3/s (5,800 cu ft/s)[1] |
| • maximum | 1,650 m3/s (58,000 cu ft/s)[1] |
Klarälven ("The clear river" in Swedish[2]) is a river flowing through Norway and Sweden. Together with Göta älv, which it is called as the river has passed through the lake Vänern, thus regarded as an entity, Göta älv—Klarälven is the longest river in Scandinavia and in the Nordic countries and its Swedish part the longest river of Sweden. These two rivers also have the largest drainage basin in the same areas, 50,229 km2 (19,394 sq mi) including all the rivers that run into Vänern, of which 42,468 km2 (16,397 sq mi) is located in Sweden and 7,761 km2 (2,997 sq mi) in Norway.[3]

It emanates at the northeast side of Mount Brändstöten and flows through a couple of smaller lakes down to Lake Rogen in Härjedalen, Sweden, and then passes through the Norwegian Hedmark, where it flows through the lake Femunden. There it is known as Femundelva and Trysilelva. The rest of the river, the longest part, flows through Värmland to ultimately discharge in a delta into Vänern at Karlstad.
In its turn, Vänern drains then into Göta älv, reaching the sea at Gothenburg.
The river has historically provided significant economic benefits, providing a suitable transport route for log driving, and currently is internationally recognized as excellent sport fishing waters.
Geography and geology[edit]

The watershed of Klarälven is commonly referred to as Klarälvdalen (the Klarälv basin), where it accumulates much of its water on its journey to Vänern. Other important sources of water are the snowy mountains in the northern areas of the watershed area, providing substantial flows in the spring when the snow melts; annual floods are common.
The straight river course north of Edebäck has been classified by Sten De Geer as a "tectonic valley" as it follows the Protogine Zone—a bedrock weakness zone of Precambrian age.[4][5] During deglaciation of Scandinavia about 10,000 years before present the glacier ice retreated unevenly with the valley of Klarälven hosting a protruding ice tongue while the surrounding uplands were ice-free. The retreat of the ice left dead-ice buried in the glacifluvial sediments of the valley.[6] The river course north of Edebäck formed an ancient fjord after it became free of glacier ice and before the post-glacial rebound definitely raised the valley bottom above the sea. The river course south of Edebäck is possibly a Quaternary deflection caused by the accumulation of glacial deposits.[4]
Since the end of the last ice age, the mouth of Klarälven has moved southward from Forshaga to its current position at Karlstad,[7] and is still moving, albeit for different reasons, as the river carries substantial quantities of sand, cut from the outer edges of its meandering curves, causing the shoreline of Vänern to constantly move southward.
The heavy meandering of Klarälven results in numerous oxbow lakes, formed as a result of a too sharp curve, eventually causing the river to create a new, shorter path. An artificial islet, Gubbholmen found in central Karlstad has also been created as a result of the accumulation of 5,000 tonnes (4,900 long tons; 5,500 short tons) of sand transported each day during the spring flood.[8]
Entering the Karlstad region, the river delta splits into two main parts and eight smaller parts. The east part splits into two further main branches after passing Gubbholmen (eventually three branches). The west part splits into five branches.
In the first half of the 20th century the geography and Quaternary geology Klarälven was studied by various Swedish researchers including Alfred Elis Törnebohm, Sten De Geer and Lennart von Post. This last Quaternary geologist died in 1951 leaving his research unfinished, despite this Klarälven was by 1956 the most studied river in Sweden.[4] Åke Sundborg's 1956 outstanding PhD thesis and publication on the geomorphology and hydrology of Klarälven is considered a major reference work for river studies in Sweden.[9]
Economic importance[edit]
There are some hydroelectric power plants in the river. These are the hydroelectric power plants from south to north.
- Forshaga power plant in Forshaga,
- Dejefors power plant in Deje, 20 MW
- Munkfors power plant in Munkfors, 33 MW,
- Skymnäsforsen power plant in Skymnäsfors, 17 MW,
- Forshult power plant in Forshult, 20 MW,
- Krakerud power plant in Krakerud, 22 MW,
- Skogaforsen power plant in Skogafors 15 MW,
- Edsforsen power plant in Edsfors 9 MW
- Höljes power plant in Höljes, 130 MW.
Fishing[edit]
In recent years,[when?] the sport fishing of Klarälven has gained an international recognition for its Atlantic salmon and brown trout fisheries; these two species of fish are sought after by fly fishers. Competition for use of areas rich in the popular species is vigorous, and at high season the price of fishing licenses may be as high as 500 Swedish krona (US$68) per day. Other measures are taken to ensure the survival of the fishery, including strict rules on the minimum sizes and quantities of fish allowed to be taken, as well as the requirement that unwanted fish, such as the northern pike, be killed when caught.[10]
Although the river was a busy log driving route, it has been reported that the fish populations of Klarälven has not suffered from the heavy activity, underwater life benefited from it, especially the grayling population. When the log driving stopped in 1991, it was later reported that the beneficial effects were slowly disappearing as shore vegetation grew denser, providing a less favourable environment for the fish.[11]
As of 1997, an upper secondary school specializing in sport fishing education was established to meet the demands for skilled professionals to guide fishing tourism.[12]
Other tourism[edit]
Klarälven has clean and fresh water, suitable for bathing, although caution must be taken if bathing at a point before the river reaches its delta, as the currents can be treacherous.[citation needed]
Modern day tourist attractions in addition to sport fishing include canoeing, as well as rafting from Branäs to Edebäck.
Log driving[edit]


Log driving has been traced back to the 17th century, although log driving increased to a significant level at the beginning of the 20th century, when the paper industry started to expand. Log driving was accomplished by dumping the harvested logs into the river, there they floated until the separation point at Forshaga. They were then held up by a floating structure resembling a fence until loggers could move out on the logs, identify them and guide them to their designated areas using special hooks. After grouping logs with the same company marks together, the logs would then be towed to their destinations.[13]
As many as 1,500 people were working seasonally, employed by the local log drivers' society, paid by the paper mills and forest owners. Although a risky job, the personnel were skilled and only one drowning incident was reported in the last 30 years of operation.[11] Out of the 19 Lusten boats used to tow the logs to their final destinations, only one remains in working condition today; Lusten 8, serving as a tourist attraction.[14]
After the shutdown of the log driving industry in 1991, the remaining equipment was auctioned off, most was sold to the Forshaga Municipality, who used the equipment to found the log driving museum, using the old buildings used for the operations as its main building. Upon the shutdown of the flood driving in Klarälven, the practice of log driving in Sweden had officially come to its end.
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d "Klarälven". Nationalencyklopedin (in Swedish). Retrieved 14 July 2010. (subscription required)
- ^ Page 168 of the Swedish Etymological Dictionary Svenskt ortnamnslexikon, published 2003 by the institute of Språk- och folkminnesinstitutet, Uppsala: The name Klarälven or Clara älv has been used since the beginning of the 18th century. Before that time the river had some other names, among them the most important name: Gautelfr i.e. Göta älv.
- ^ Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute (in Swedish) Archived 2018-09-28 at the Wayback Machine (Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute).
- ^ a b c Sundborg, Åke (1956). "The River Klaralven: A Study of Fluvial Processes". Geografiska Annaler. 38 (3): 238–316. doi:10.2307/520285. JSTOR 520285.
- ^ Andréasson, Per-Gunnar; Rodhe, Agnes (1992). The Protogine Zone. Geology and mobility during the last 1.5 Ga (PDF) (Report). SKB technical report.
- ^ Lundqvist, Jan (2003). "Deglaciation Pattern in Subaquatic: Supra-Aquatic Transitional Environment Illustrated by the Klarälven Valley System, Värmland, Western Sweden". Geografiska Annaler. 85 (1): 73–89. doi:10.1111/1468-0459.00190. S2CID 140586387.
- ^ History of Forshaga published by the Genealogy Society of Värmland
- ^ Dubbskadeexkursion den 22 juni[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Kungl. Vetenskapsakademiens årsberättelse 2007" (PDF) (in Swedish). No. 81. Stockholm. 2008. pp. 30–31. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-07-04. Retrieved 2016-10-25.
{{cite magazine}}: Cite magazine requires|magazine=(help) - ^ Rules for sport fishing Archived 2005-12-06 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Lundén, Bo. Flottningen på Klarälven (1986)
- ^ SportfiskeAkademin - om skolan Archived 2007-03-11 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Flottningens historia Archived 2007-09-28 at the Wayback Machine on Museum of Värmland
- ^ Forshaga kanal Archived 2006-02-21 at the Wayback Machine
