Hair whorl
| Hair whorl | |
|---|---|
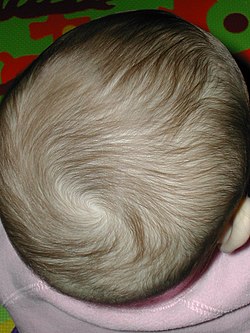 Human baby hair whorl | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vortices pilorum |
| TA98 | A16.0.00.026 |
| FMA | 76564 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
A hair whorl is a patch of hair growing in a circular direction around a visible center point. Hair whorls occur in most hairy animals, on the body as well as on the head. Hair whorls, also known as crowns, swirls, or trichoglyphs, can be either clockwise or counterclockwise in direction of growth.
In human theories[edit]
Hair whorls on the head (parietal whorls) have been studied by some behaviorists. Most people have clockwise scalp hair-whorls. Parietal whorls which are considered to be normal scalp patterns could be a single whorl or double whorls. Cases of triple parietal whorls are less common.
Amar J. S. Klar conducted research to see if there was a genetic link between handedness and hair-whorl direction. He found that 8.4% of right-handed people and 45% of left-handed people have counterclockwise hair-whorls. His research suggested that a single gene may control both handedness and hair-whorl direction.[1] However, Klar's research methodology in this and other studies has been questioned.[2]
The direction of hair whorl is not consistent with Blaschko's lines.[3]
Another result concerning handedness of the progeny of discordant monozygotic twins suggests that left handed people are one gene apart from right handed people. Together, these results suggest (1) that a single gene controls handedness, whorl orientation, and twin concordance and discordance and (2) that neuronal and visceral (internal organs) forms of bilateral asymmetry are coded by separate sets of genetic pathways.[4]
Animal behavioral theories[edit]

There are many (mostly apocryphal) theories concerning horse behavior and their hair whorls.[5]
One paper has suggested that abnormal hair whorls can be used to assess the likelihood of agitated behavior or temperament in cattle in the auction ring.[6]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Human handedness and scalp hair-whorl direction develop from a common genetic mechanism. Klar AJS Genetics 2003 Sep 165(1):269-76 http://www.genetics.org/cgi/reprint/165/1/269.pdf
- ^ "Myths of Human Genetics: Hair Whorl". udel.edu. Retrieved 2019-01-14.
- ^ Happle, Rudolf; Assim, Atessa (April 2001). "The lines of Blaschko on the head and neck". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 44 (4): 612–615. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.112386. PMID 11260527.
- ^ Klar, Amar J. S. (2003-09-01). "Human Handedness and Scalp Hair-Whorl Direction Develop From a Common Genetic Mechanism". Genetics. 165 (1): 269–276. doi:10.1093/genetics/165.1.269. ISSN 1943-2631. PMC 1462764. PMID 14504234.
- ^ Forsberg Meyer, Jennifer. "What's in a Whorl?" Horse & Rider June 2008: 46-53.
- ^ A note on hair whorl position and cattle temperament in the auction ring
