Carson River
Carson River
| |
|---|---|
 Carson River at Dayton, Nevada | |
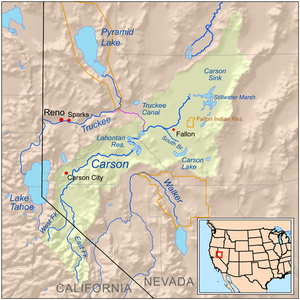 Carson River Basin | |
| Etymology | Kit Carson |
| Native name |
|
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Nevada |
| Region | central Lahontan region |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | West Fork Carson River |
| • location | Carson Pass, Alpine County, CA |
| 2nd source | East Fork Carson River |
| • location | Sonora Peak, California |
| Source confluence | mouths of West & East forks |
| • location | near Minden, Nevada |
| • coordinates | 39°42′47″N 118°39′21″W / 39.71306°N 118.65583°W[3] |
| Length | 131 mi (211 km)[4] |
| Basin size | 3,930 sq mi (10,200 km2)[5] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Carson City, NV[6] |
| • average | 400.9 cu ft/s (11.35 m3/s)[6] |
| • minimum | 1.96 cu ft/s (0.056 m3/s) |
| • maximum | 30,500 cu ft/s (860 m3/s) |
The Carson River is a northwestern Nevada river that empties into the Carson Sink, an endorheic basin. The main stem of the river is 131 miles (211 km) long[4] although the addition of the East Fork makes the total length 205 miles (330 km), traversing five counties: Alpine County in California and Douglas, Storey, Lyon, and Churchill Counties in Nevada, as well as the Consolidated Municipality of Carson City, Nevada. The river is named for Kit Carson, who guided John C. Frémont's expedition westward up the Carson Valley and across Carson Pass in winter, 1844.[7] The river made the National Priorities List (NPL) on October 30, 1990 as the Carson River Mercury Superfund site (CRMS) due to investigations that showed trace amounts of mercury in the wildlife and watershed sediments.[8]
History[edit]
Archaeological findings place the eastern border for the prehistoric Martis people in the Reno/Carson River area, these are thought to be the first humans to enter the area about 12,000 years ago. By the early 1800s, the Northern Paiute lived near the lower Carson River and the present Stillwater National Wildlife Refuge, while the Washoe people inhabited the upper watershed region.[9]
The Carson River watershed was a shared territory between these two tribes. The Northern Paiute of western Nevada was grouped into several bands relating to the area that they inhabited. The group that established itself along the Carson River were known in the Shoshone language as "Toituked".[10] The Washoe peoples that had residence in the Carson Valley were also divided into a separate group and called "Pau wa lu".[11] Ancient people and indigenous tribes used the Carson River as a resource for livelihood, depending on the river for fish, waterfowl, plant materials, and especially water in the arid Nevada desert climate.[12] Displacement of these tribes and changes of lifestyle did not take place until the development of European settlements.
The first European settlements in Nevada were the 1851 settlements at Mormon Station (now Genoa) and at the mouth of Gold Canyon (Dayton), both in the Carson River Watershed. In the 1850s and 1860s, the river was used as the route of the Carson Trail, a branch of the California Trail that allowed access to the California gold fields, as well as by the Pony Express. Gold was discovered along the river in the Silver Mountain Mining District in 1860.[13] 1868 Virginia and Truckee Railroad transported ore to the quartz reduction mines along the river.[14] Virginia City, Nevada, along the lower watershed, was home to the world's greatest silver rush, the Comstock Lode in 1859. The Carson Valley provided food and forage for the silver miners and their livestock. The Comstock mining boom critically impacted the watershed and water quality by causing deforested slopes, mine tailings, and steep raw riverbanks above channels cut into the valley floor in many places.[9] These mining operations have also led to high levels of existing mercury concentrations within the watershed.[15]
In the early 20th century, the Newlands Reclamation Act was passed to bring irrigation water into the region for agriculture. The Lahontan Dam, completed in 1914, was constructed as part of the Newlands Irrigation Project.[16] The Truckee-Carson Irrigation District was formed in 1918 as part of the project to divert water from the Truckee River to the Carson Valley for agricultural use.
In 1989, the East Fork Carson River was designated a "Wild and Scenic River" by the State of California from Hangman's Bridge just east of Markleeville, California to the CA/NV border, prohibiting any further consideration of impoundment.[17]
Watershed[edit]
The 205 miles (330 km) Carson River watershed encompasses 3,966 square miles (10,270 km2)[9] and includes two major forks in the Sierra Nevada in its upper watershed region. The 74-mile-long (119 km)[4] East Fork[18] rises on the north slopes of Sonora Peak (itself just north of Sonora Pass at about 10,400 feet (3.2 km) in southern Alpine County, southeast of Markleeville in the Carson-Iceberg Wilderness. The 40-mile-long (64 km)[4] West Fork[19] rises in the Sierras near Carson Pass and Lost Lakes at 9,000 feet (2,700 m) elevation and flows northeast into Nevada, joining the East Fork about 1 mile (1.6 km) southeast of Genoa. The Carson River then flows north 18 miles (29 km) to the end of the upper watershed at Mexican Dam[20] just southeast of Carson City. In the middle watershed, the river runs generally northeast from Carson City across Lyon County, past Dayton. The middle watershed ends in eastern Churchill County at the Lahontan Dam.[21] Here, river flows are augmented by water from the Truckee River and stored in the Lake Lahontan reservoir. Downstream from the dam (in the lower watershed), much of the water is used for irrigation in the vicinity of Fallon, with limited flows continuing northeast into the Carson Sink.
Clear Creek, which begins at about 8,780 feet (2,680 m) on Snow Valley Peak (Toiyabe National Forest, Carson Range) west of Carson City, is the only perennial tributary of the Carson River mainstem, and is protected by the Nature Conservancy.[22][23]
Carson River mercury superfund site[edit]
The Carson River basin, from New Empire to Stillwater and the Carson Sink, was designated as National Priority Listed (NPL) due to historic mining activity site under the Comprehensive Environmental Response Compensation and Liability Act (CERCLA or Superfund) in August 1990. This is Nevada's only NPL site and is being jointly managed by NDEP and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency 9 (EPA), Region IX, in San Francisco.[24] Millions of pounds of mercury were imported and used in approximately 250 Comstock mills to recover gold and silver. An estimated 14,000,000 pounds of mercury was lost to the environment during that process. Arsenic and lead, which were common constituents of the mined ore, were concentrated by the milling process and were also released into the environment. Therefore, the contaminants of concern (CoCs) at the site are mercury, arsenic, and lead.
Mercury, arsenic, and lead are known or suspected carcinogens (cancer-causing agents) and/or detrimental to human health in some other way. Mercury is the primary concern regarding the Carson River Mercury Superfund site. Several forms of mercury are prevalent in the open water source, including inorganic mercury (Hg2+) and organic methylmercury (MeHg). MeHg is produced from bacteria in river systems and can be ingested by the wildlife in the area. The methylmercury, due to its specific properties that include it being fat soluble, can lead to bioaccumulation and biomagnification of mercury in Carson River Aquatic wildlife.[25] The contaminants, however, need a route into the human body to have a harmful effect. Direct contact with soils and subsequent ingestion and/or eating fish and waterfowl taken from the CRMS area, which may have already ingested CoCs, provide the most likely route into the body. Small children have the highest risk due to developing bodies and their propensity for ingesting soil while at play. Signs of Mercury poisoning due to oral ingestion are most commonly found to affect kidneys, central nervous system, and development - especially in organic mercury.[26] The EPA and other scientists studied residents of contaminated areas and found no direct evidence of increased metals in blood, hair and urine samples. They did find elevated levels in certain fish and waterfowl. Some of the highest levels in the nation. Human health, if impacted, would be impacted slowly, over years of small amounts of exposure, and could be hard to detect.
The upland (dry-land) contamination source area of the CRMS. OU-1 is undergoing continued management and monitoring to assure public protection from mine wastes. The most significant health risk in OU-1 is direct contact and ingestion of contaminated soils. OU-2 is defined as the water, sediment, and biologic resources of the Carson River, Lahontan Reservoir, Washoe Lakes, Steamboat Creek, associated irrigation ditches, and the Stillwater Wildlife Refuge. EPA Contractor and USGS are continuing studies of OU-2 areas and will produce a (RI/FS)[clarification needed]. The most significant health risk posed by mercury in OU-2 is the consumption of fish and waterfowl from affected lake and river systems. In the 1990s, the EPA compelled several limited area cleanups to be completed by third parties and completed cleanup on a half dozen areas themselves. The cleanups occurred primarily in residential areas of Dayton. The remainder of the site has not undergone cleanup, and due to the size and scope of the area impacted, most likely never will. Since complete site cleanup is not economically viable. A long-term sampling and response plan (LTSRP) was developed to manage site contamination in the future. The LTSRP provides guidance for land development activities (both commercial and residential) to help assure site CoCs do not impact human health and the environment. Typically, soil sampling is required to verify developed area soils do not contain CoCs at levels which may cause harm to human health.[27]
Mercury amalgamation process[edit]
The Mercury in the Carson river is primarily introduced into the river through sediment deposition resulting from mine tailings during the Comstock Lode. These tailings were attributed to the mining process that settlers used in the 1850s to recover silver and gold. This process is known as mercury amalgamation. Mercury amalgamation has been mining precious metals since the Middle Ages. Mercury amalgamation is accomplished by pulverizing the ore and covering it with mercury using drums or tables. Once the mercury binds to the gold or silver, it is separated from the barren soil to a retorting vessel where the mercury is vaporized and condensed off of the amalgam.[28] During the Comstock Lode a new, Washoe "hot-pan" amalgamation, the process was created specifically to treat Nevada ore in 1861. Washoe "hot pan" mining used a cast iron pan with the soil mixture, mercury, sulfuric acid, and other materials to remove the precious metals.[29]
Losses of mercury that attributed to the contamination of the Carson River and eventually to the CRMS occurred during these processes. Mercury loss in the mining operations ranged from transportation failures, crude equipment, and poor handling. The mercury was transferred using leather bags, pails, and barrels that leaked and spilled. Equipment was not up to standards and not practical for containing tailings. However, most of the mercury loss happened throughout the amalgam process. The recovery amount of the vaporized mercury completely depends on the technology used, and the efficiency of mercury binding depends on the ability of the precious metal. Both of the actions were not completely refined themselves and attributed to as much as 0.7–1 kg of mercury waste/ per tonne of ore processed in Nevada mines.[29]
Hydraulic mining was also used in the Carson River region. Hydraulic mining uses mercury to bond to the gold and silver in the mining slurry. The gold/silver amalgam drops to the bottom of the sluice while gravel and other tailings pass over. As time passes, the mercury is ground into a fine layer that coats the bottom of the sluice and can contaminate the surrounding area through leaks and the effluent of water containing the mercury. It is estimated that this practice in California attributed to mercury losses up to 10-30%.[30]
Ecology[edit]

In the lower reaches of the Carson River watershed, the Stillwater National Wildlife Refuge hosts large breeding colonies of white-faced ibis (Plegadis chihi) and is frequented by non-breeding American white pelicans (Pelecanus erythrorhynchos). In winter, the refuge supports wintering tundra swans (Cygnus columbianus) as well as hosts of ducks and geese. The Carson River watershed also provides habitat for many smaller species of birds such as tree swallows (Tachycineta bicolor) and house wrens (Troglodytes aedon). Recent research on these two bird species has shown significant mercury concentrations in the livers and eggshells of the birds nesting along the river.[15]
The upper Carson River watershed provides habitat for the threatened Lahontan cutthroat trout (Oncorhynchus clarki henshawi), as well as large non-native rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and brown trout (Salmo trutta), providing excellent fly fishing. The Lahontan cutthroat is threatened by hybridization with rainbow trout, but there is a pure Lahontan strain on 5 miles (8.0 km) of the East Fork Carson River from the headwaters to Carson Falls.[13] There is also a native population of the only Paiute cutthroat trout (Oncorhynchus clarki seleniris) in existence in the drainages of Silver King Creek, a tributary of the East Fork Carson River in the Carson Ranger District of the Humboldt-Toiyabe National Forest.
North American beaver (Castor canadensis) were re-introduced to the Carson River watershed around 1940 and have thrived since. There are eyewitness accounts of beaver in the upper Carson River through 1892.[31] The Washo people who lived in the eastern Sierra with hunting grounds extending as far west as Calaveras County, have a word for beaver, c'imhélhel.[32][33] Powers reported that the northern Paiute wrapped their hair in strips of beaver fur, made medicine from parts of beaver and that their creation legend included beaver, which they called su-i'-tu-ti-kut'-teh.[34] Given the hydrological connection of the Humboldt River and Sink to the Carson Sink during flood years (as recently as 1998), it is not surprising that beavers were historically extant on eastern Sierra watercourses.[35] Peter Skene Ogden, on a Hudson's Bay Company expedition to the terminus of the Humboldt River, wrote in his diary on May 15, 1829, "In no part have I found beaver so abundant. The total number of American trappers in this region at this time exceeds 80. I have only 28 trappers... The trappers now average 125 beaver a man and are greatly pleased with their success."[36] James "Grizzly" Adams trapped beaver in the Carson River around 1860, "In the evening we caught a fine lot of salmon-trout (cutthroat trout), using grasshoppers for bait, and in the night killed half a dozen beavers, which were very tame."[37] Adams' account is consistent with a 1906 newspaper article in the Nevada State Journal that the Mason's Valley of the nearby Walker River in Yerington, Nevada was well known to "the early trappers and fur hunters...Kit Carson knew it to the bone...The beavers of course were all trapped long ago, and you never see an elk nowadays..."[38]
Environmental impact[edit]
During the Comstock Lode mining operations (1860-1890), extensive amount of Mercury (Hg) was released into the Carson River, Lahontan Reservoir, and Stillwater National Wildlife Refuge.[39] The mercury levels in the Carson River and Lahontan Reservoir vary from 100-1000 ng/L, which is considered highly toxic.[39] The surrounding wildlife has been exposed to this contamination and has been subject to negative effects. These organomercurials readily bioaccumulate and affect the predators in this ecosystem with the greatest mercury concentration. An example of this bioaccumulation has been researched in fish-eating birds along the river. The species involved in the study were adult double-crested cormorants (Phalacrocorax auritus), snowy egrets (Egretta thula) and black-crowned night-herons (Nycticorax nycticorax), which all recorded high levels of Hg toxicity in their kidneys and livers.[40] Concentrations of Hg were also observed in eggs and fledglings, but were found not to affect the hatchability of the eggs. Rather, the levels of mercury observed in fledglings have led to induced stress, immune deficiencies, and neurological impairment, which could lead to a decrease in survival rates for younger birds learning to survive along the Carson River.[40]
Many fish species in the Carson River also have been studied to check for mercury contamination. In one study, electrofishing was conducted at four different locations along the river to capture and sample fish for traces of Hg toxicity.[41] Carp, golden shiners, species of sucker-fish, and crayfish all showed Hg toxicity in samples taken from the four testing sites. This study also showed that many samples taken from the fourth, and furthest down the river system, produced higher levels of Hg contamination, suggesting that the mercury has been getting washed down the Carson River and accumulating at the Lahontan Reservoir.[41] White bass,a piscivorous species in Lahontan Reservoir, are subject to the bioaccumulation of Hg contamination, and have showed mercury concentration significantly higher to that catfish species found in the reservoir due to difference in diet. Research has shown that the concentrations of mercury vary dependent on species, diet, and size of the individual fish, and that currently the fish found in the reservoir are considered safe, but not recommended, for human consumption.[42]
Recreation[edit]
The Carson River is a trophy trout stream that offers ideal conditions for both fly and spinning anglers. Further up in the river system anglers can fish for various species of trout, such as the previously mentioned Lahontan Cutthroat, Rainbow, and Brown trout. Down the river system the ecosystem changes to a warm water environment, and the fish species change accordingly.
Backcountry hiking is found along the upper river in the Carson-Iceberg Wilderness. Kayakers and river rafters enjoy the lower river's gentle class II rapids, as well as its outstanding scenery and river-side hot springs. The East Carson has extensive Native American cultural values associated with the Washoe tribe. The watershed is also a popular recreation spot for mountain biking, off-roading, hunting, and horse-back riding. Development along the river in Douglas, Carson City, and Lyon counties has limited public access in some areas.
See also[edit]
- Carson River Canyon
- Beaver in the Sierra Nevada
- Carson Range
- List of California rivers
- List of Nevada rivers
References[edit]
- ^ SWCA Environmental Consultants (2002). "Northern Paiute and Western Shoshone Land Use in Northern Nevada: A Class I Ethnographic/Ethnohistoric Overview" (PDF).
- ^ Washoe Cultural Resource Office (2009). "Wa She Shu: "The Washoe People" Past and Present" (PDF).
- ^ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Carson River (GNIS feature ID 859159)
- ^ a b c d U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. The National Map Archived 2012-03-29 at the Wayback Machine, accessed March 17, 2011
- ^ "USGS Water Resources: About USGS Water Resources".
- ^ a b "USGS Surface Water data for USA: USGS Surface-Water Monthly Statistics".
- ^ Federal Writers' Project (1941). Origin of Place Names: Nevada (PDF). W.P.A. p. 19.
- ^ "CARSON RIVER MERCURY SITE Site Profile". cumulis.epa.gov. Retrieved 2020-12-11.
- ^ a b c Carson River Watershed Map (PDF) (Report). University of Nevada, Reno. Retrieved 2012-12-09.
- ^ Park, Willard Z. (Willard Zerbe), 1906-1965. (1989). Willard Z. Park's ethnographic notes on the Northern Paiute of western Nevada, 1933-1940. Fowler, Catherine S. Salt Lake City, Utah: University of Utah Press. ISBN 0-585-29276-0. OCLC 45732746.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Resources Office, The Washoe Cultural (2009). "WA SHE SHU: "The Washoe People" Past and Present" (PDF). United States Forest Service. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-11-01. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- ^ "Washoe Tribe of California and Nevada | ONE". onlinenevada.org. Archived from the original on 2021-01-22. Retrieved 2020-12-09.
- ^ a b David Loomis (July 2007). East Carson River Strategy (PDF) (Report). USDA Forest Service. p. 43. Retrieved 2012-12-09.
- ^ Drew, Stephen. "Virginia & Truckee History". Archived from the original on 2011-07-17. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ a b Custer, Christine M.; Custer, Thomas W.; Hill, Elwood F. (2006-11-02). "Mercury Exposure and Effects on Cavity-Nesting Birds from the Carson River, Nevada". Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 52 (1): 129–136. doi:10.1007/s00244-006-0103-6. ISSN 0090-4341. PMID 17083002. S2CID 25407881.
- ^ "Carson Water Subconservancy District". Archived from the original on 2013-01-14. Retrieved 2012-12-09.
- ^ "California Rivers: East Carson River". California Rivers. Archived from the original on 2007-01-25. Retrieved 2012-12-09.
- ^ "East Fork Carson River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior.
- ^ "West Fork Carson River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior.
- ^ "Mexican Dam". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior.
- ^ "Lahontan Dam". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior.
- ^ "Clear Creek". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior.
- ^ "Clear Creek: Partnering for Protection". Nature Conservancy. Archived from the original on 2013-07-16. Retrieved 2012-12-09.
- ^ "Carson River Mercury Superfund Site | NDEP". ndep.nv.gov. Retrieved 2018-07-25.
- ^ Flickinger, Allison. “Impact of Potential Climate Change on Predicted Fluvial Transport of Mercury and Associated Bioaccumulation along the Carson River-Lahontan Reservoir System.” University of Nevada - Reno, UMI, 2015.
- ^ ATSDR (March 3, 2011). "Toxic Substances Portal - Mercury". Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Archived from the original on 2009-03-30. Retrieved October 26, 2020.
- ^ "Carson River Mercury Superfund Site June 2012" (PDF).
- ^ "Mercury Amalgamation". mine-engineer.com. Retrieved 2020-12-09.
- ^ a b Nriagu, Jerome O. (1994-06-20). "Mercury pollution from the past mining of gold and silver in the Americas". Science of the Total Environment. 149 (3): 167–181. Bibcode:1994ScTEn.149..167N. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(94)90177-5. hdl:2027.42/31497. ISSN 0048-9697.
- ^ N. Alpers, Charles (2000). "Mercury Contamination from Historic Gold Mining in California" (PDF). USGS. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-04-10. Retrieved December 9, 2020.
- ^ Tappe, Donald T. (1942). "The Status of Beavers in California" (PDF). Game Bulletin No. 3. California Department of Fish & Game. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-27. Retrieved 2010-10-28.
- ^ A. L. Kroeber (1919). "30". Handbook of Indians of California. Retrieved 2010-08-19.
- ^ "The Washo Project". University of Chicago. Retrieved 2010-08-19.
- ^ Don D. Fowler; Catherine S. Fowler; Stephen Powers (Summer–Autumn 1970). "Stephen Powers' "The Life and Culture of the Washo and Paiutes"". Ethnohistory. 17 (3/4): 117–149. doi:10.2307/481206. JSTOR 481206.
- ^ Weimeyer, S. N. (2001). Humboldt River and Humboldt Wildlife Management Area Contaminant Monitoring (Report). USFWS, Reno Field Office. Archived from the original on 2010-03-26. Retrieved 2010-10-28.
- ^ Peter Skene Ogden. "Journal of Peter Skene Ogden; Snake Expedition, 1828-1829". London, England: Hudson's Bay Company House. Retrieved 2010-10-28.
- ^ Theodore Henry Hittell (1861). The adventures of James Capen Adams: mountaineer and grizzly bear hunter, of California. Crosby, Nichols, Lee and company. p. 250. Retrieved 2011-12-24.
salmon-trout.
- ^ Fitz-James MacCarthy (1906-02-18). "Wonderful Deposits of High-Grade Rock". Nevada State Journal. Retrieved 2011-07-10.
- ^ a b Wayne, David M.; Warwick, John J.; Lechler, Paul J.; Gill, Gary A.; Lyons, W. Berry (1996-12-01). "Mercury contamination in the Carson River, Nevada: A preliminary study of the impact of mining wastes". Water, Air, and Soil Pollution. 92 (3): 391–408. Bibcode:1996WASP...92..391W. doi:10.1007/BF00283569. ISSN 1573-2932. S2CID 92055274.
- ^ a b Henny, Charles J.; Hill, Elwood F.; Hoffman, David J.; Spalding, Marilyn G.; Grove, Robert A. (2002-08-01). "Nineteenth Century Mercury: Hazard to Wading Birds and Cormorants of the Carson River, Nevada". Ecotoxicology. 11 (4): 213–231. doi:10.1023/A:1016327602656. ISSN 1573-3017. PMID 12211695. S2CID 31980313.
- ^ a b Pesticides Monitoring Journal. Technical Services Division, Office of Pesticide Programs, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 1975.
- ^ Pesticides Monitoring Journal. Technical Services Division, Office of Pesticide Programs, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 1975.
External links[edit]
- Rivers of the Sierra Nevada in California
- Rivers of Nevada
- Rivers of the Sierra Nevada in Nevada
- Rivers of the Great Basin
- Rivers of Churchill County, Nevada
- Rivers of Douglas County, Nevada
- Rivers of Lyon County, Nevada
- Rivers of Storey County, Nevada
- Humboldt–Toiyabe National Forest
- Pony Express
- Rivers of the Sierra Nevada (United States)
- Rivers of Carson City, Nevada

