CSS Richmond
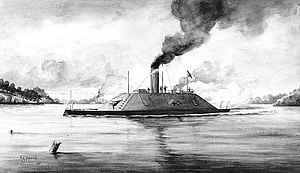 A wash drawing of Richmond by R. G. Skerrett
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | Richmond |
| Namesake | Richmond, Virginia |
| Operator | Confederate States Navy |
| Ordered | 1862 |
| Builder |
|
| Laid down | March 1862 |
| Launched | 6 May 1862 |
| Commissioned | July 1862 |
| Fate | Burned and scuttled, 3 April 1865 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type | Richmond-class ironclad |
| Length | |
| Beam | 43 ft (13.1 m) |
| Draft | 12–13 ft (3.7–4.0 m) |
| Depth | about 11 ft (3.4 m) |
| Installed power | 2 × fire-tube boilers |
| Propulsion |
|
| Speed | 6 knots (11 km/h; 6.9 mph) |
| Complement | 150 officers and men |
| Armament |
|
| Armor | |
CSS[Note 1] Richmond was the name ship of her class of six casemate ironclads built for the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War. Completed during 1862 the ship was assigned to the James River Squadron where she mostly supported Confederate forces near Richmond, Virginia. She was burned in April 1865 to prevent her capture by Union forces.
Background and description[edit]
The ship was built to a design by the Chief Naval Constructor, John L. Porter, based on his earlier work on the ironclad CSS Virginia, retaining the traditional curving ship-type hull, but with flat ends to the casemate. As usual for Confederate ships, dimensions vary slightly between sources. The plan showed an overall length of 174 feet (53.0 m) and a length between perpendiculars of 150 feet (45.7 m) with a maximum beam of 43 feet (13.1 m), a moulded beam of 32 feet (9.8 m) and a depth of hold of about 11 ft (3.4 m).[2] The consensus figure for the ship's draft is 12 to 13 feet (3.7 to 4.0 m)[3][4][5] She was fitted with a pilothouse at the forward end of the casemate roof.[6]
The propulsion systems of the Richmond-class ironclads were different for each of the ships, often depending on what could be sourced locally. Richmond's single-cylinder, 80-horsepower direct-acting steam engine had been stored in the Gosport Navy Yard when the brig Arctic was converted to a lightship in 1859. Seized when the Confederates captured the Navy Yard, the engine used steam provided by a pair of horizontal fire-tube boilers built by either the Tredegar Iron Works or the Shockoe Foundry in Richmond to drive a three-bladed, 9-foot (2.7 m) propeller. The boilers were 11 feet (3.4 m) tall, 10 feet (3.0 m) long, and 6 feet 9 inches (2.1 m) wide.[7][Note 2] Richmond had a speed of 6 knots (11 km/h; 6.9 mph) and a crew of 150.[3] She also carried about 20 to 25 Confederate States Marines in case of a battle that required naval boarding.[9]
Richmond was armed with four 7-inch (178 mm) Brooke rifles, one of which was two banded (reinforced at the breech) and the others were single-banded guns.[10] Two of the guns were on pivot mounts at the bow and stern and the others were positioned on each broadside.[11] The ship was also equipped with a spar torpedo at her bow.[3][12] Other sources concur with the total of four guns, but state that they consisted of one 7-inch Brooke rifle in the bow, two 6.4-inch (163 mm) Brooke rifles on the broadsides, and a 10-inch (25.4 cm) muzzle-loading smoothbore gun on a pivot mounting in the stern.[5][12] Naval historian Raimondo Luraghi states that the ship was armed with four 7-inch Brooke rifles and two smoothbores,[13] while official historian Paul Marcello simply notes that the ship was equipped with four rifled guns and two smoothbore shell guns.[3]
Sources agree that Richmond's 100-foot-long (30.5 m) casemate was protected by 4 inches (102 mm) of wrought-iron armor in two layers of plates. The casemate structure consisted of 21 inches (530 mm),[12] 22 inches (560 mm)[5][13] or 23 inches (580 mm) of oak and yellow pine. The roof of the casemate was covered by 1-inch (25 mm) iron plates, backed by 15 inches (380 mm) of wood.[11] One layer of two-inch plates protected the fore and aft main decks and extended below the waterline for several feet.[12] A 10-inch iron casting supposedly defended the pilothouse.[6]
Construction and career[edit]
Named for the capitol of the Confederacy,[14] Richmond was begun at Gosport Navy Yard in March 1862, launched on May 6 and towed up to her namesake that very night to escape Federal forces threatening the yard and the lower James River. She was sometimes referred to as Virginia II, Virginia No. 2 or Young Virginia in the South and as Merrimack No. 2, New Merrimack or Young Merrimack by Union writers, months before the actual CSS Virginia II was ever laid down. The ironclad was thus finished at Richmond, Virginia, in July 1862 and placed in commission by Commander Robert B. Pegram, as part of the James River Squadron.
During 1863 and early 1864 the James front was quiet, but from May 1864 momentous events followed in quick succession. The Confederate Navy had three new ironclads in Captain French Forrest's James River Squadron there, and minor actions were frequent.
During 1864 Richmond, under Lieutenant William Harwar Parker, CSN, took part in engagements at Dutch Gap on August 13, Fort Harrison on September 29 – October 1, and Chaffin's Bluff on October 22. On January 23–24, 1865, she was under heavy fire while aground with Virginia II above the obstructions at Trent's Reach — at an angle that caused Federal projectiles to ricochet harmlessly off their casemates. But Richmond's unarmored tender, CSS Scorpion, being lashed alongside Richmond, was severely damaged by the explosion of CSS Drewry's magazine. The ironclads were forced to withdraw under the Confederate batteries at Chaffin's Bluff. A few weeks later, however, Richmond had to be destroyed to avoid capture by order of Rear Admiral Raphael Semmes, squadron commander, prior to the evacuation of the Confederate capital on April 3.
Commanders[edit]
The commanders of the CSS Richmond were:[15]
- Commander Robert B. Pegram (November 1862 – May 1864)
- Commander William Harwar Parker (May–June 1864)
- Lieutenant John S. Maury (July–October 26, 1864)
- Commander William A. Webb (October–November 1864)
- Commodore John McIntosh Kell (December 30, 1864-February 1865)
- Lieutenant Hamilton Henderson Dalton (February 1865-)
- Passed Midshipman J.A. Peters (during February 1865)
Notes[edit]
Citations[edit]
- ^ Silverstone, p. xviii
- ^ Canney, pp. 34, 40–41
- ^ a b c d Marcello
- ^ Bisbee, p. 87; Holcombe, p. 16
- ^ a b c Silverstone 2006, p. 152
- ^ a b Canney, p. 39
- ^ Canney, p. 41, Bisbee, p. 189
- ^ Luraghi, p. 48, footnote 147
- ^ Coski, p. 113
- ^ Coski, p. 80
- ^ a b Canney, p. 41
- ^ a b c d Holcombe, p. 17
- ^ a b Luraghi, p. 208
- ^ Silverstone 1984, p. 52
- ^ Coski, pp.
References[edit]
- Bisbee, Saxon T. (2018). Engines of Rebellion: Confederate Ironclads and Steam Engineering in the American Civil War. Tuscaloosa, Alabama: University of Alabama Press. ISBN 978-0-81731-986-1.
- Coski, John M. (2005) [1996]. Capital Navy: The Men, Ships and Operations of the James River Squadron. New York: Savas Beatie. ISBN 1-932714-15-4.
- Canney, Donald L. (2015). The Confederate Steam Navy 1861-1865. Atglen, Pennsylvania: Schiffer Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7643-4824-2.
- Holcombe, Robert (1978). "The Richmond Class Confederate Ironclads" (PDF). Confederate Historical Association of Belgium News. 6: 16–20. Retrieved June 19, 2022.
- Marcello, Paul J. (November 13, 2015). "Richmond 1862–1865". Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. Naval History and Heritage Command. Retrieved June 19, 2022.
- Silverstone, Paul H. (2006). Civil War Navies 1855–1883. The U.S. Navy Warship Series. New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-97870-X.
- Silverstone, Paul H. (1984). Directory of the World's Capital Ships. New York: Hippocrene Books. ISBN 0-88254-979-0.
- Still, William N. Jr. (1985) [1971]. Iron Afloat: The Story of the Confederate Armorclads. Columbia, South Carolina: University of South Carolina Press. ISBN 0-87249-454-3.
